Introduction
We recently got our hands on a new ultra-slim magnetic power bank from Xiaomi. Despite being equipped with a 5000mAh battery, the device maintains an impressively slim profile at just 8.7mm thick. It features a high-strength aluminum casing with a finely sandblasted finish, making it both lightweight and refined. The USB-C port supports 20W input and 22.5W output for fast two-way wired charging, along with 15W wireless charging capabilities.
Next, let’s take it apart to examine its internal components and structure.
Product Appearance

The front of the packaging box features the Xiaomi logo, the product name, and an image of the device.

The back of the packaging displays the spec info.
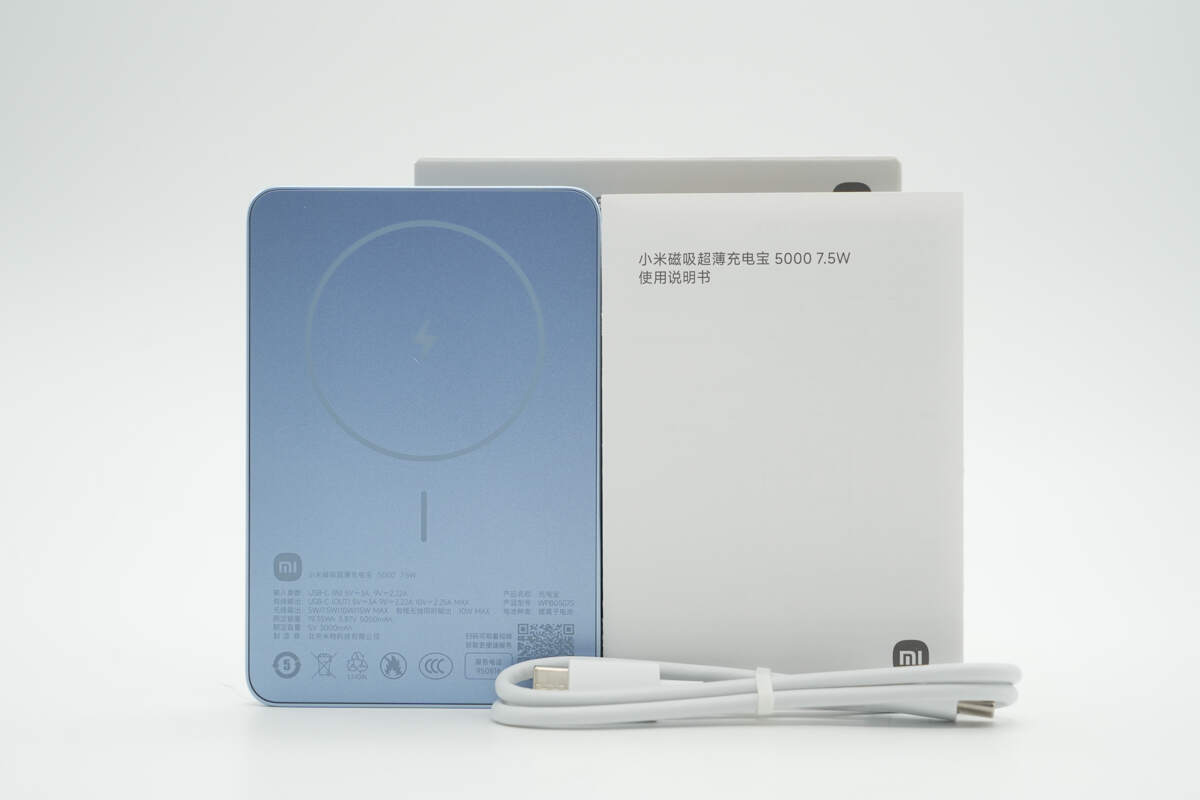

The packaging contains the power bank, cable, and some documents.

The included charging cable is a dual USB-C type.
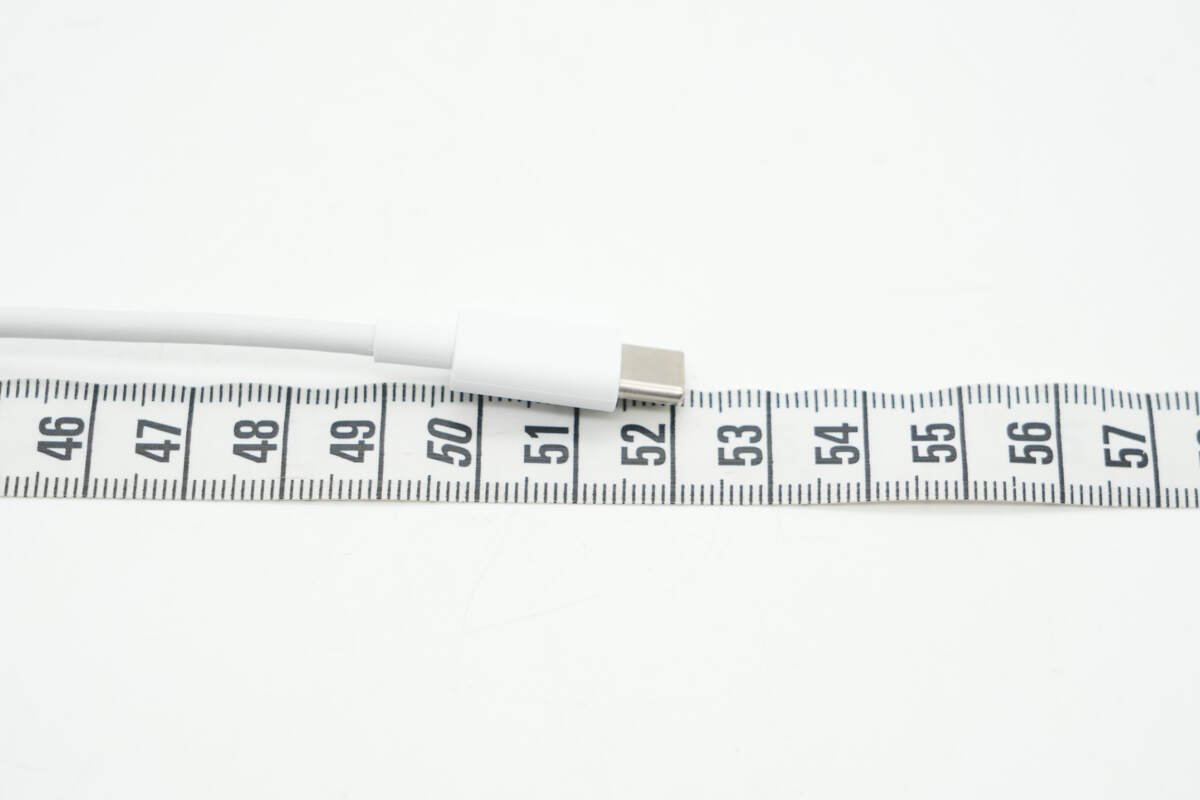

The length of the cable is about 52 cm (20.47 inches).
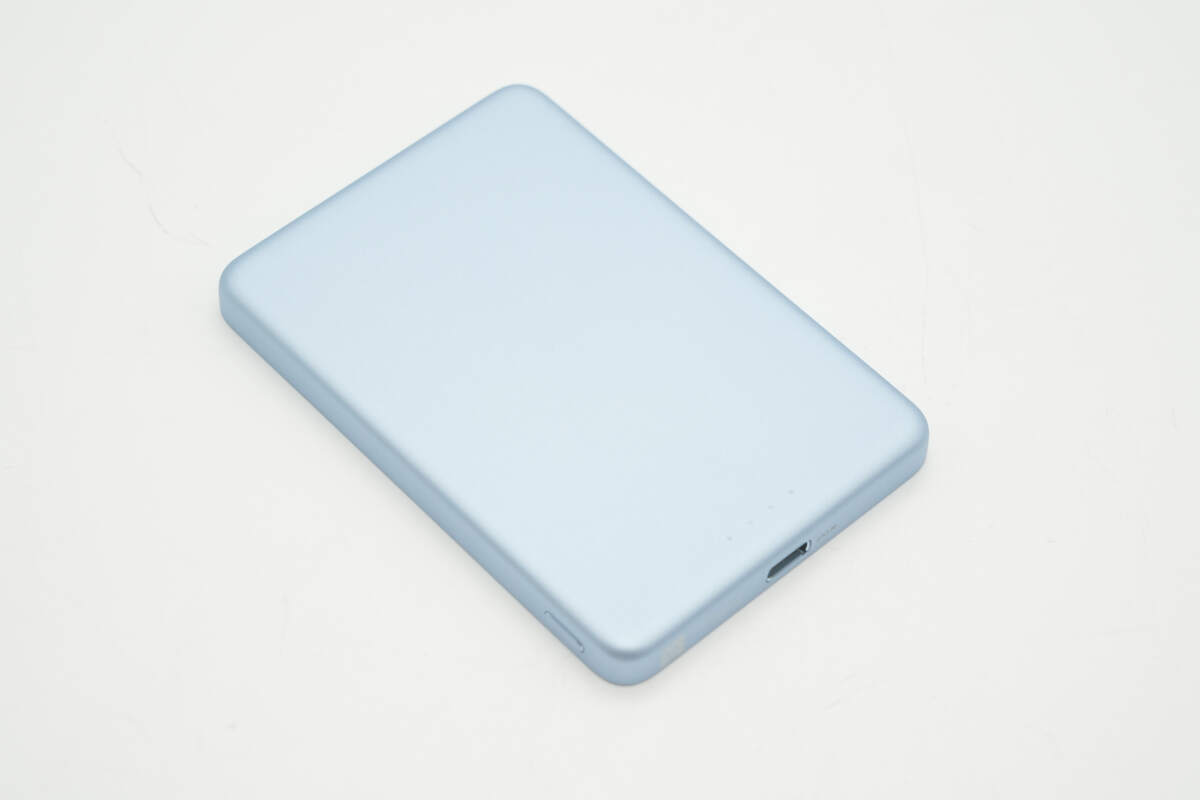

It features a high-strength aluminum casing combined with precision sandblasting, giving it a refined appearance and a smooth, premium feel in the hand.
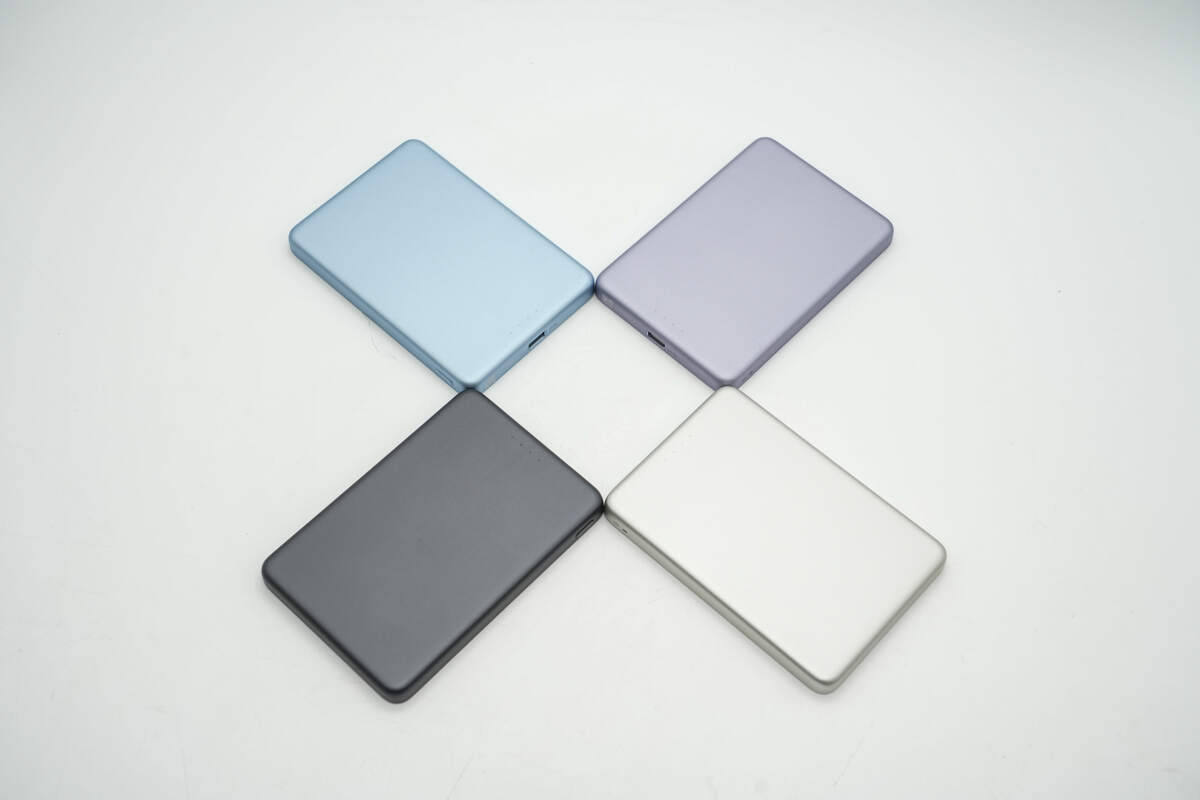

This model is available in four color options: gold, purple, blue, and black.
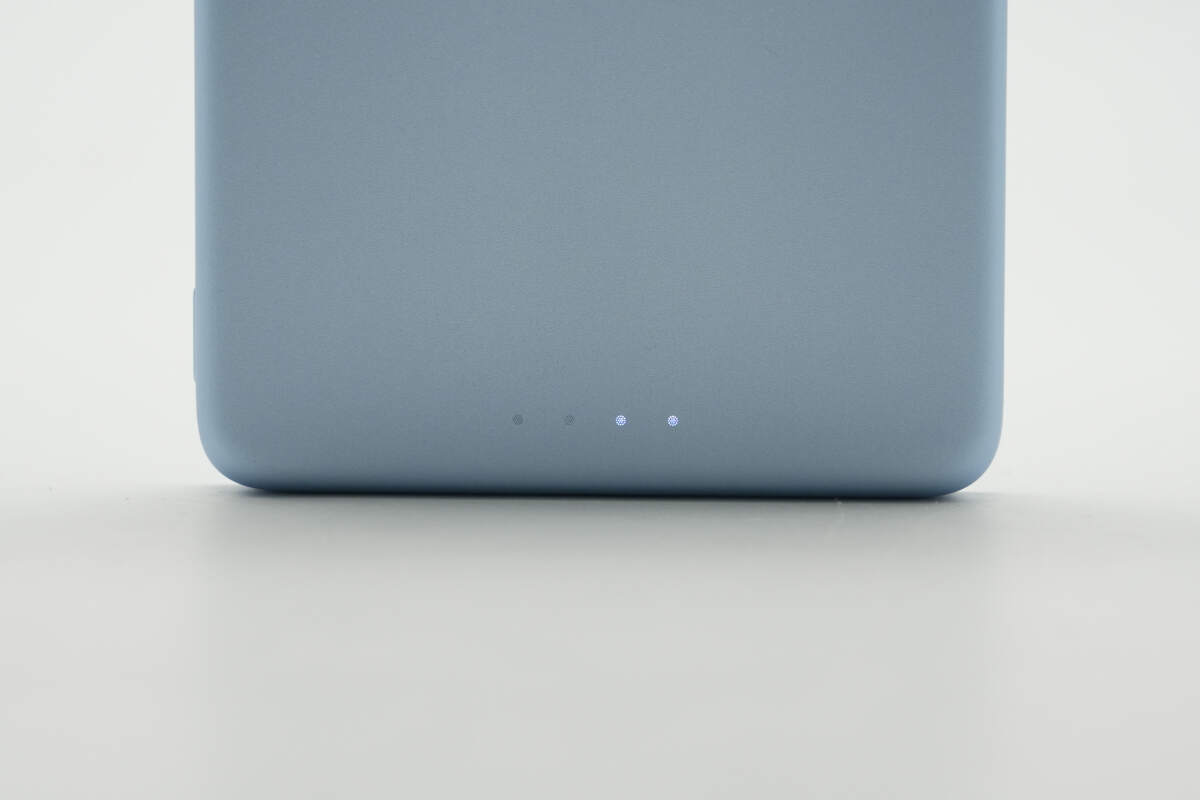

There is a battery level indicator light located at the bottom of the front side.
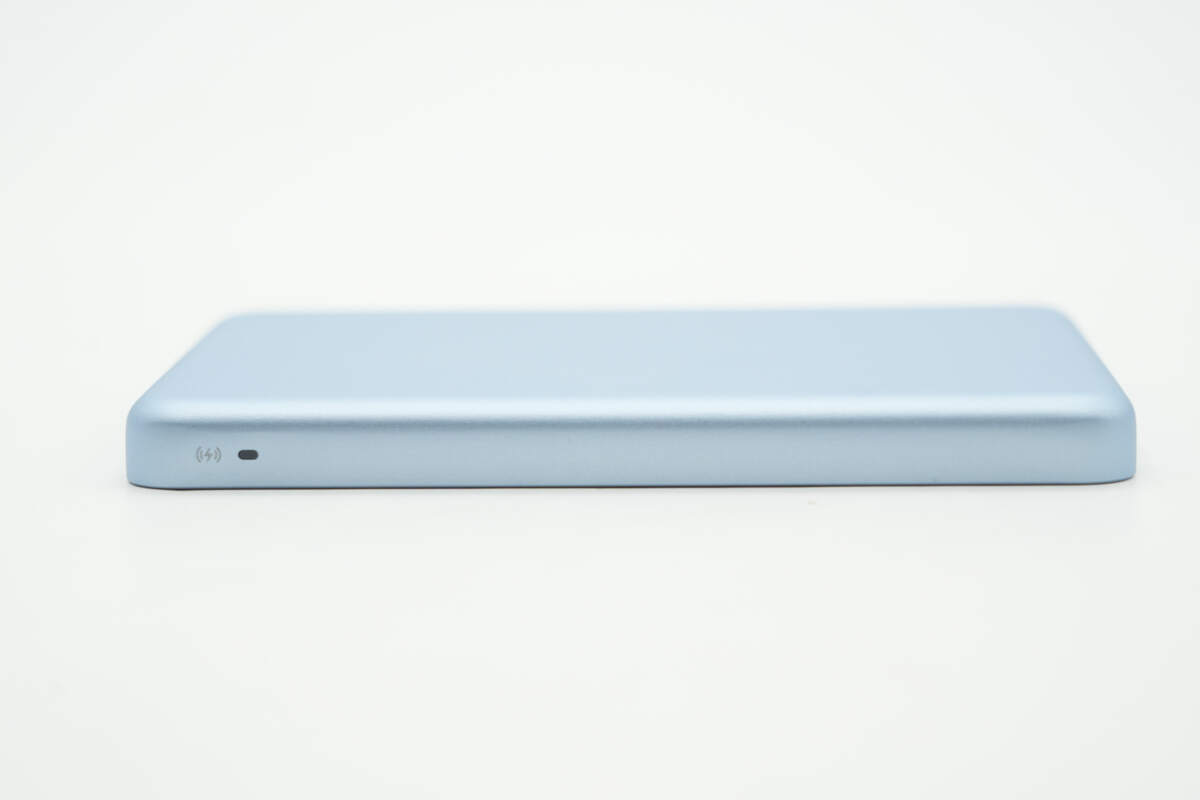

There is a wireless charging indicator light on the side.
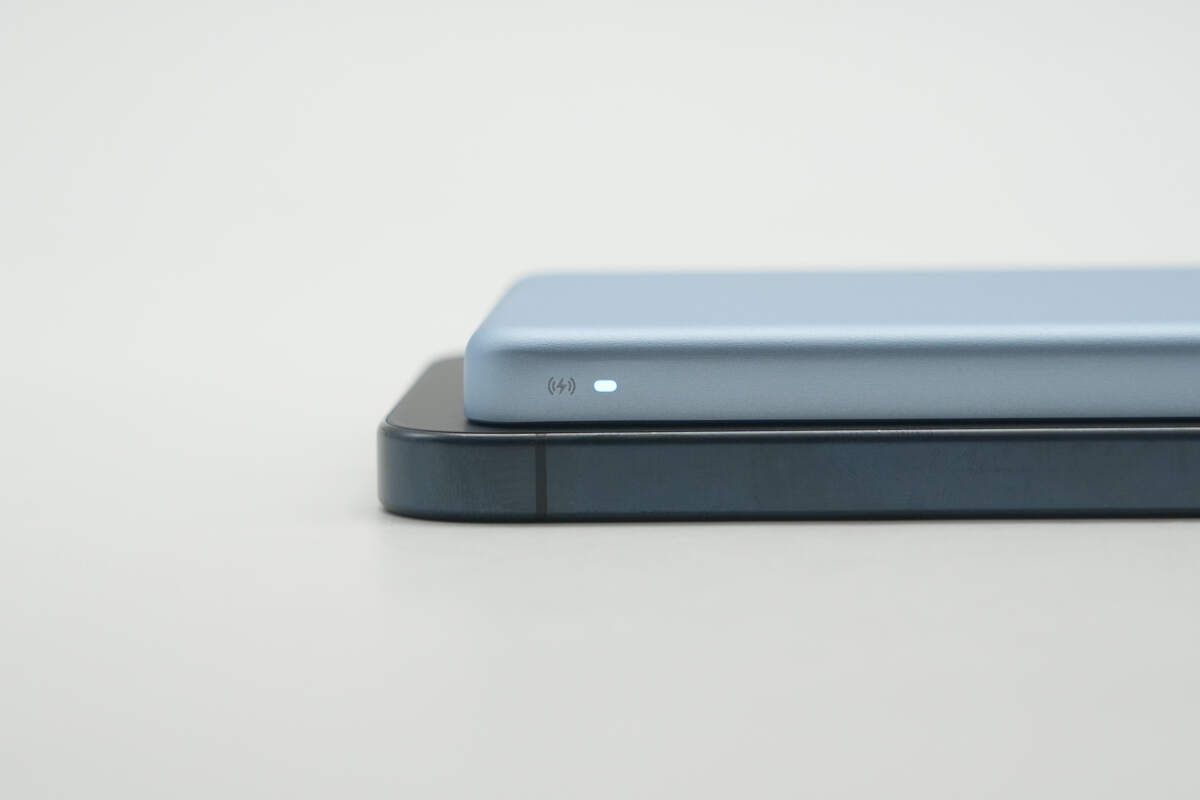

When wirelessly charging a phone, the indicator light emits a white glow.
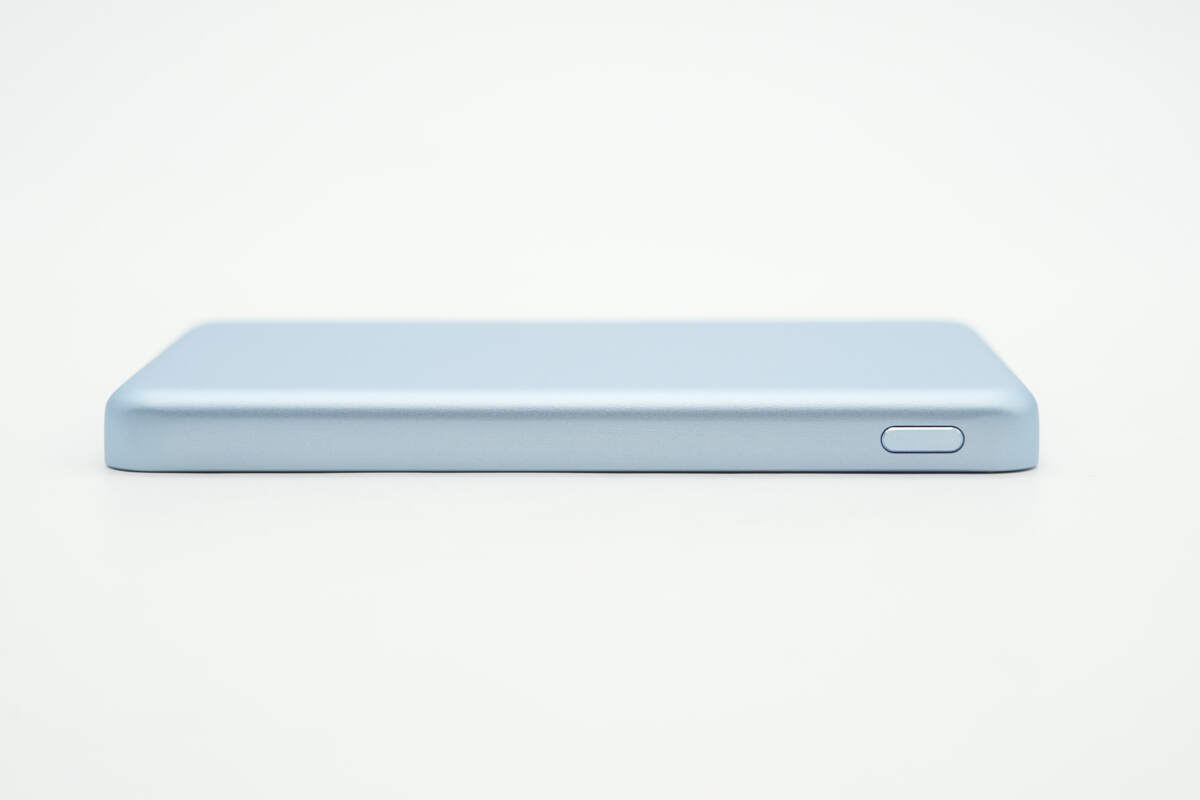

A power button is located on the opposite side.

The magnetic side features a lightweight yet durable fiberglass panel.

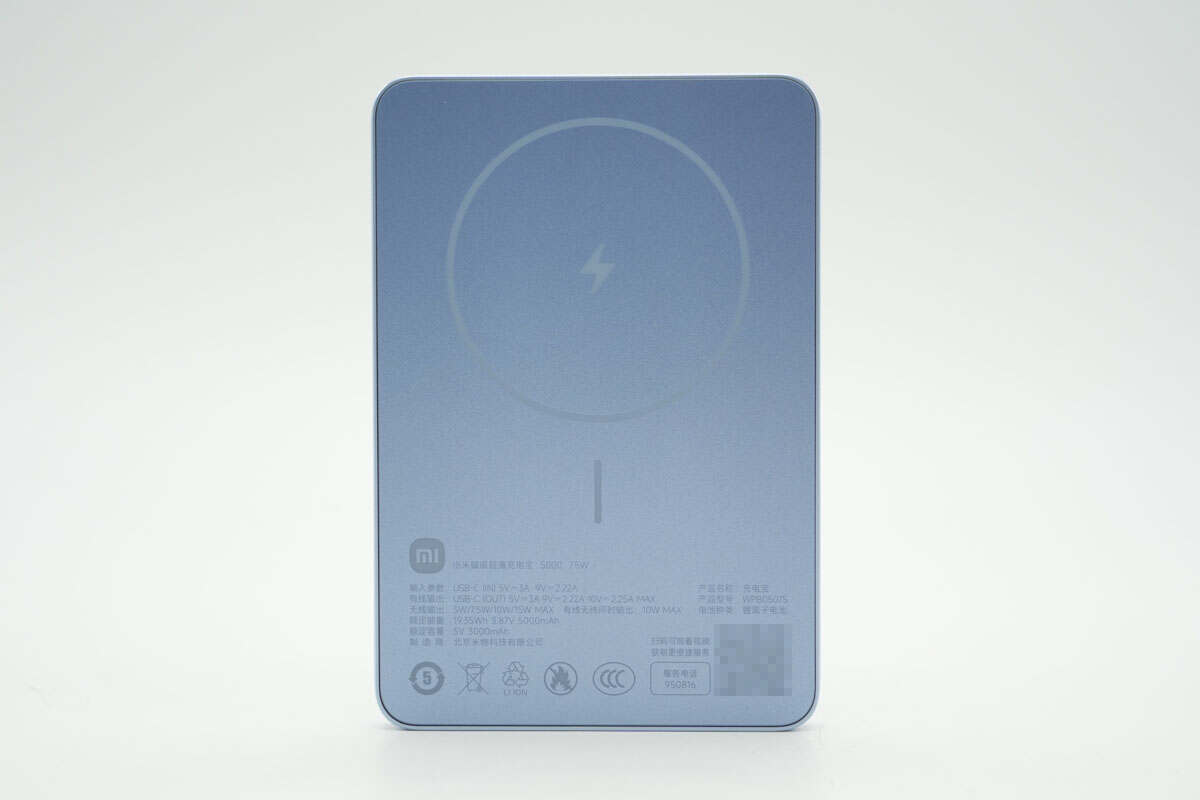
There is a wireless charging area indicator on the top.

On the lower part, the product parameters are laser-engraved:
Battery type: Lithium-ion battery
Rated energy: 19.35Wh, 3.87V, 5000mAh
Rated capacity: 5V 3000mAh
Model number: WPB0507S
Input (USB-C IN): 5V/3A, 9V/2.22A
Wired output (USB-C OUT): 5V/3A, 9V/2.22A, 10V/2.25A max
Wireless output: 5W/7.5W/10W/15W max
Simultaneous wired and wireless output: 10W max
The product has passed the CCC certification.
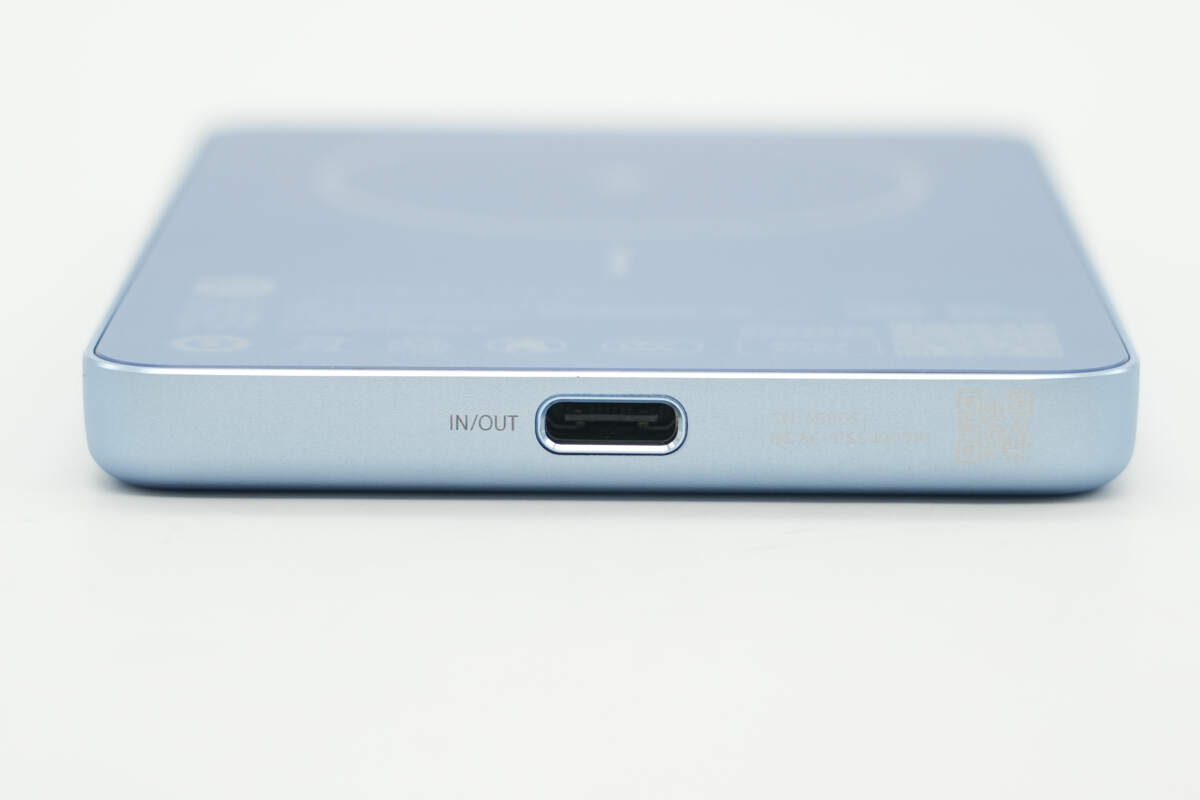

There is a USB-C port at the bottom that supports two-way fast charging.
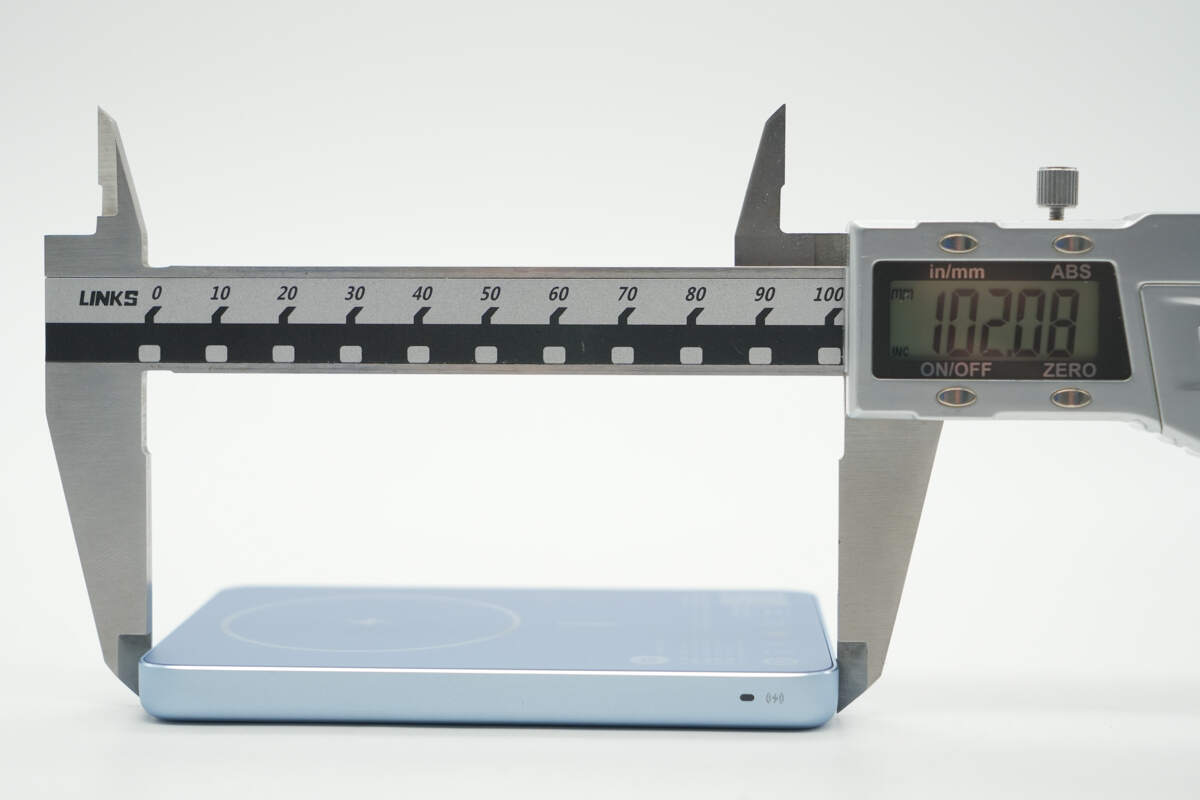

The length of the power bank is about 102.08 mm (4.019 inches).
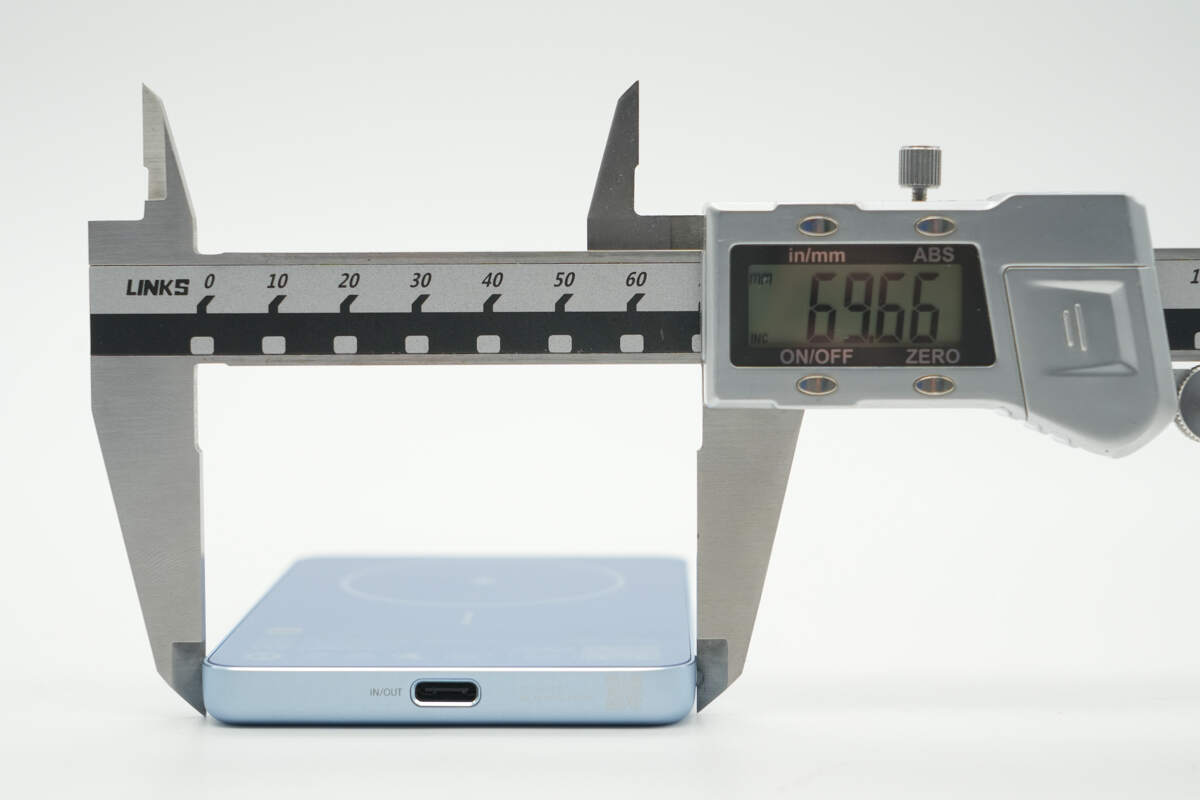

The width is about 69.66 mm (2.74 inches).
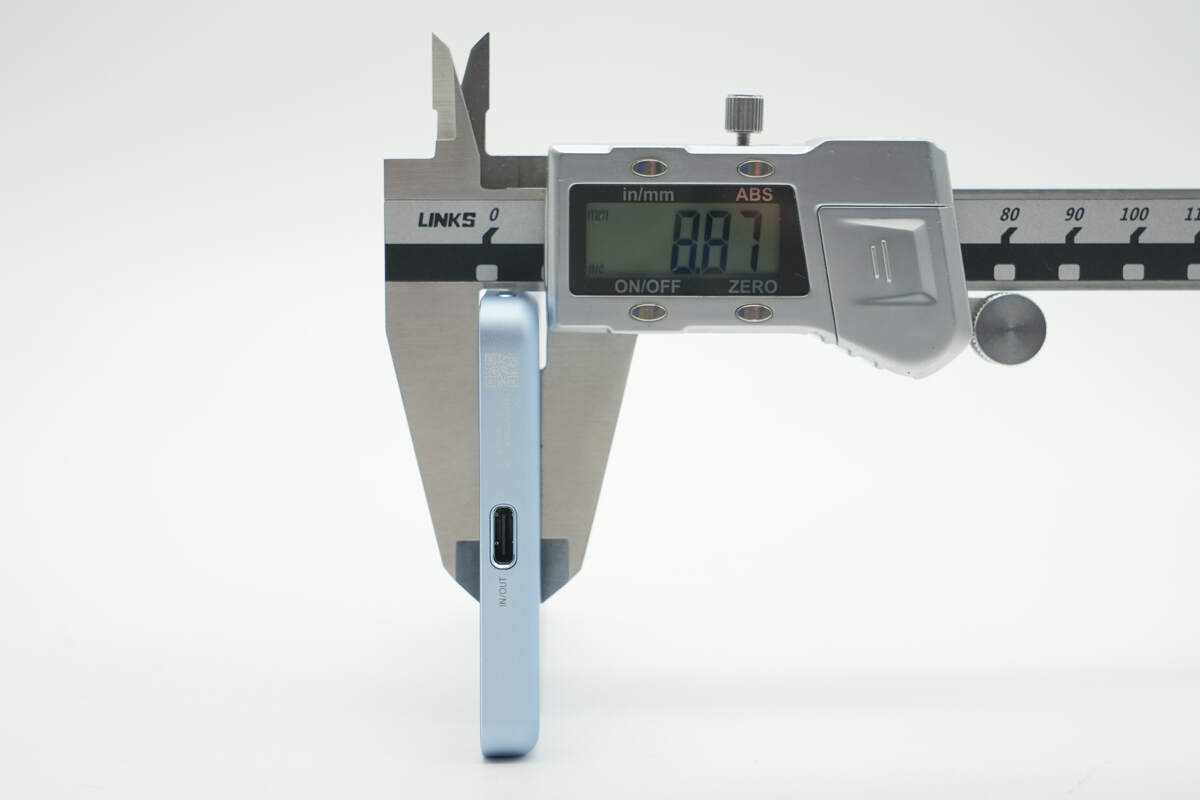

The thickness is about 8.87 mm (0.35 inches).
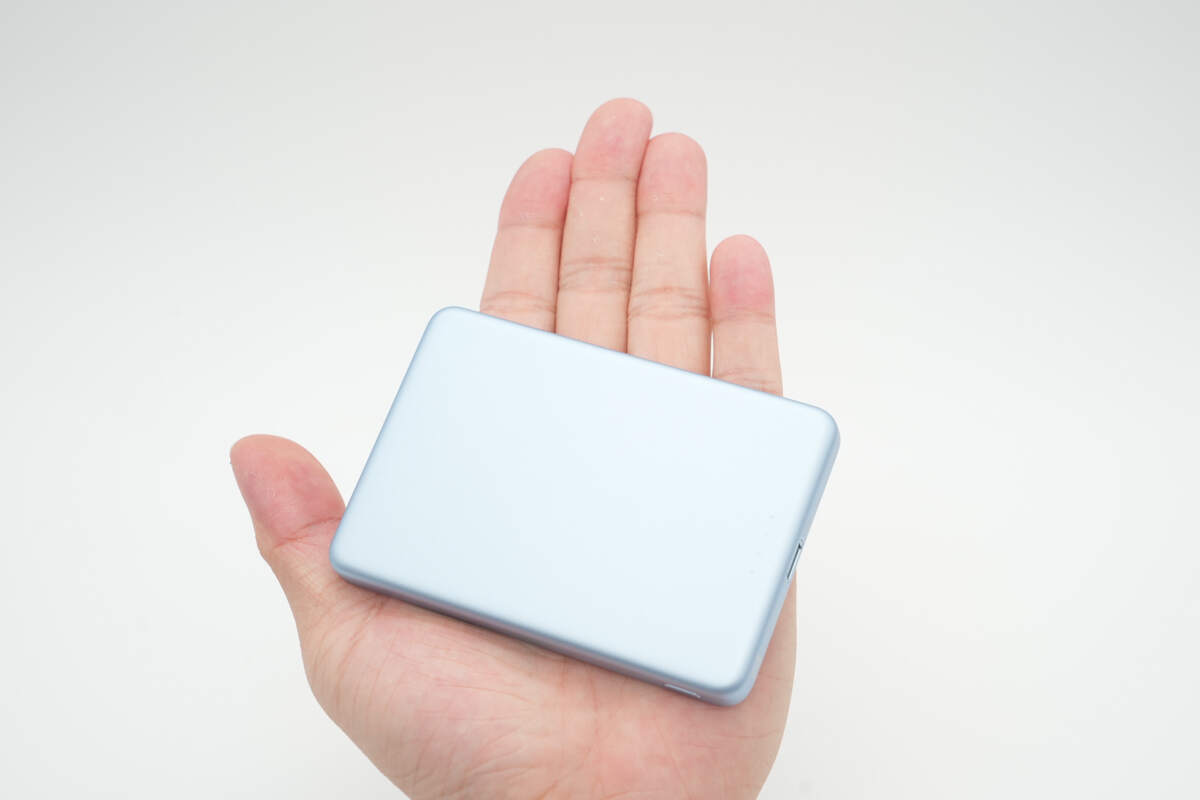

That's how big it is in the hand.
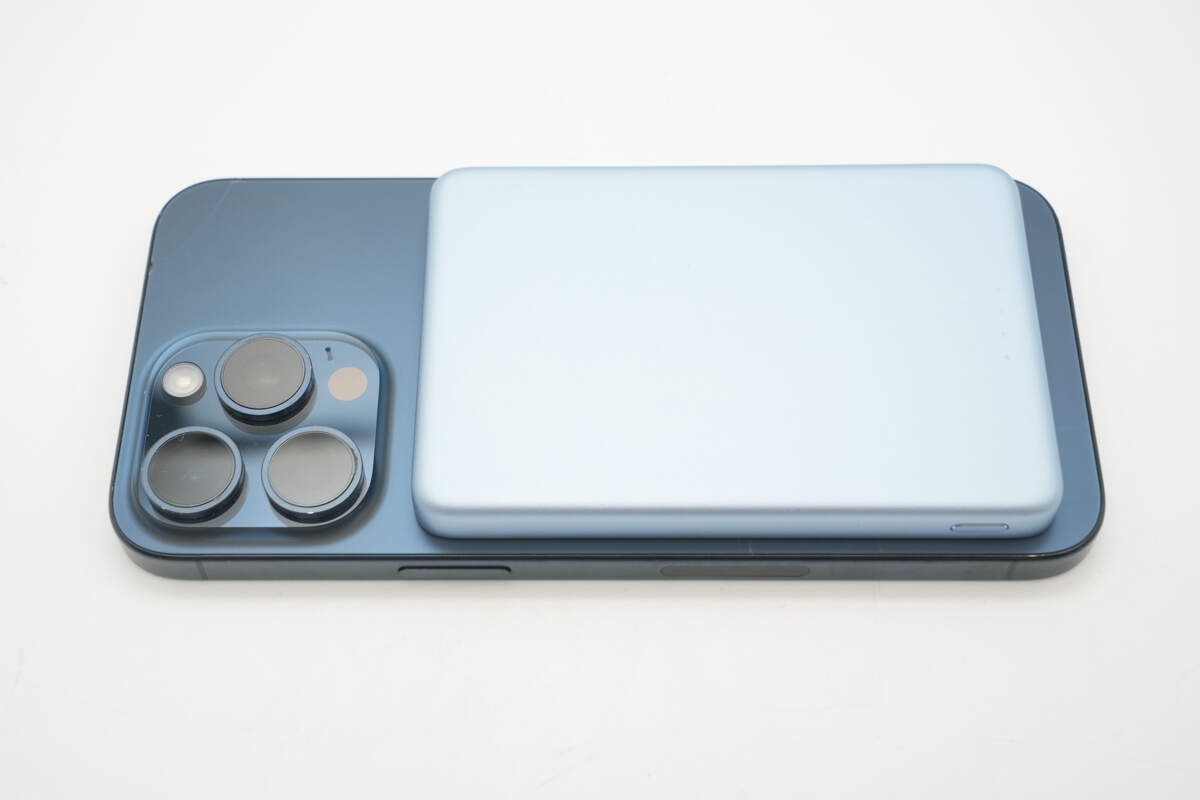

When wirelessly charging an iPhone, it does not obstruct the camera module.
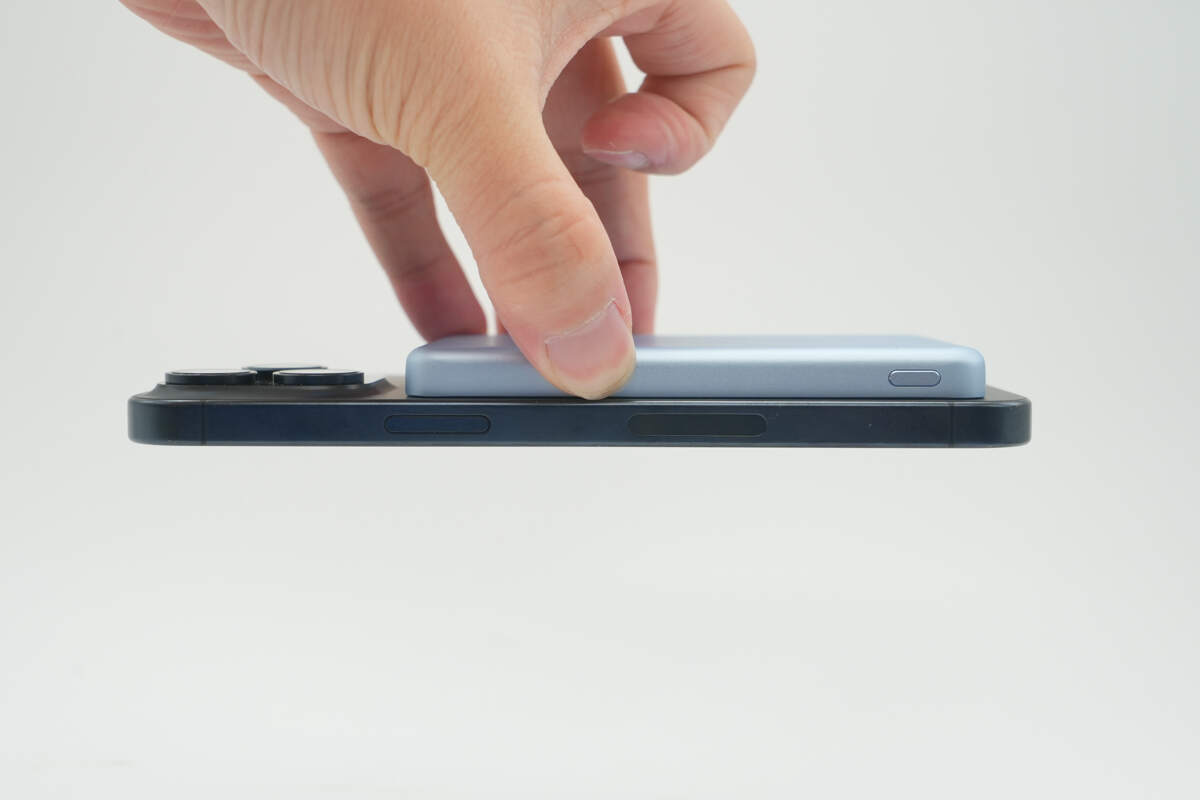

It can easily attach to the iPhone 15 Pro Max magnetically and won’t fall off even when turned upside down.
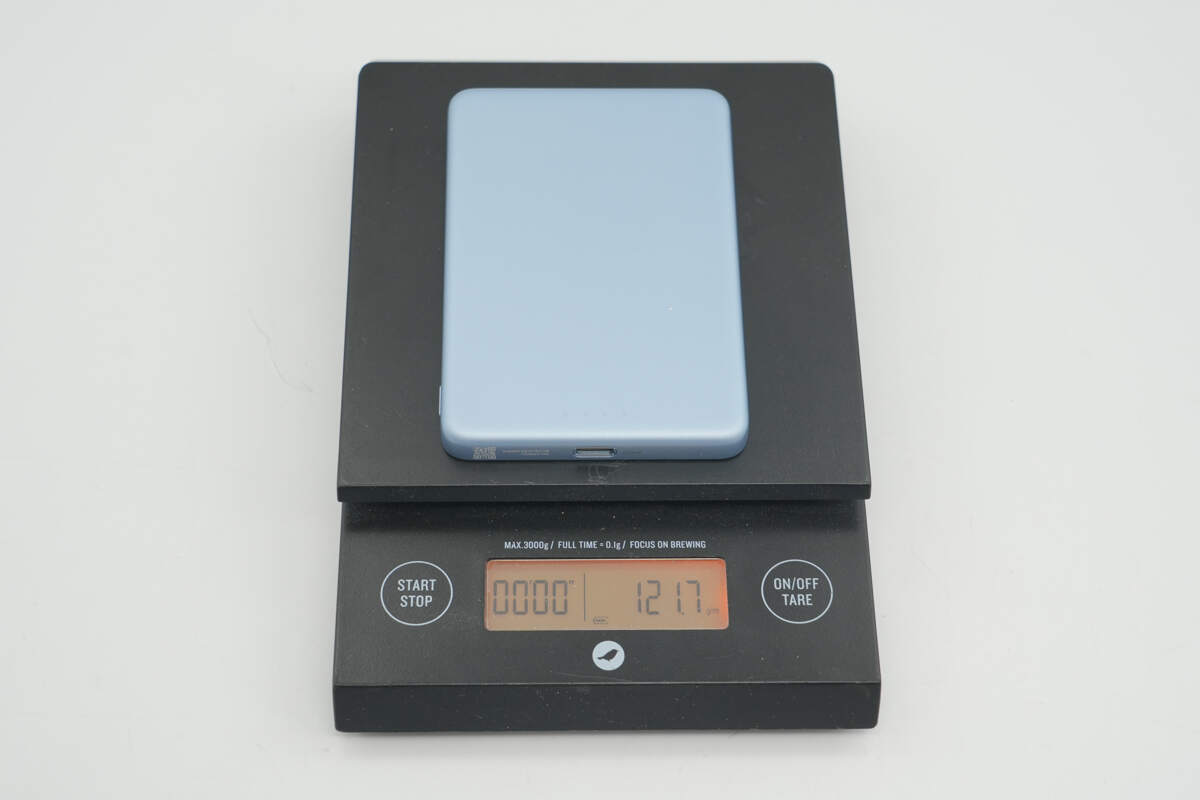

The weight is about 122 g (4.3 oz).

ChargerLAB POWER-Z KM003C shows that the USB-C supports QC3+/4+, FCP, AFC, PD3.0, PPS, DCP, and Apple 2.4A charging protocols.
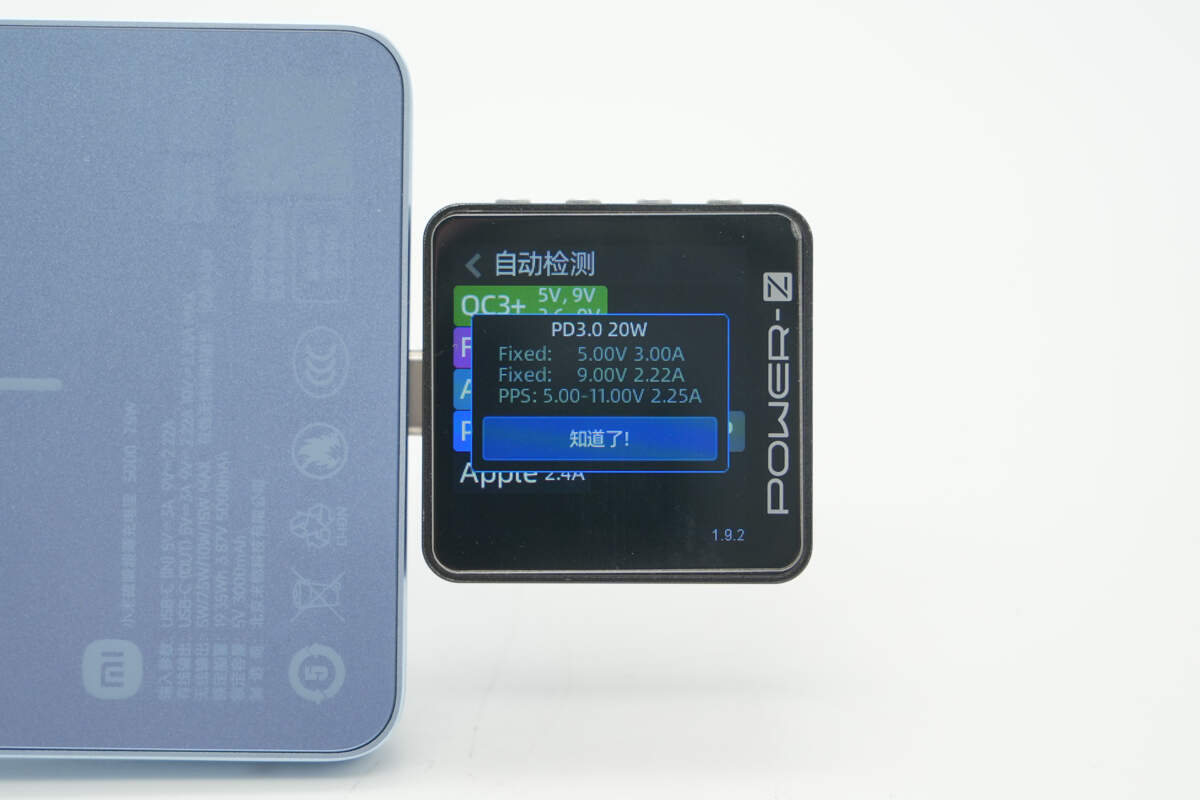

And it has two fixed PDOs of 5V3A and 9V2.22A. It has one set of PPS, which is 5-11V2.25.
Teardown
Next, let's take it apart to see its internal components and structure.
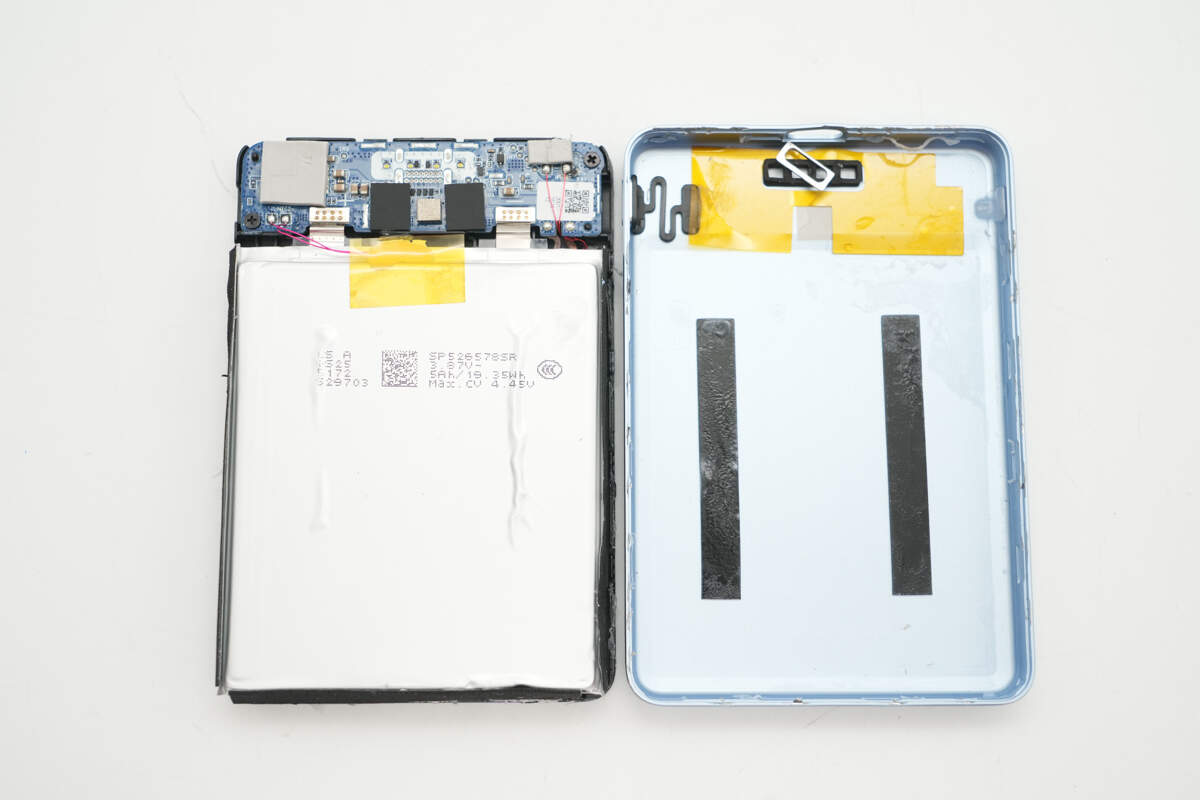

After opening the casing, you’ll find double-sided adhesive inside, and the area corresponding to the PCB is covered with insulating tape.
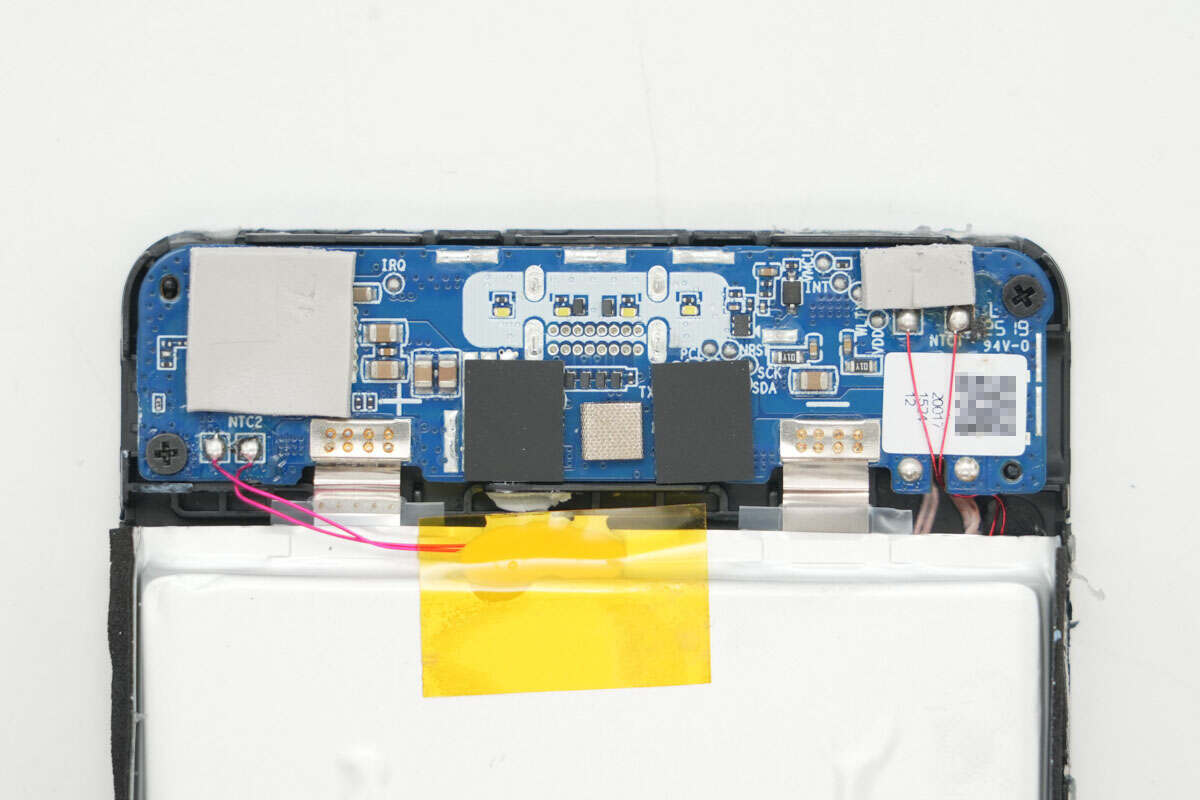
The PCB and battery cells are spot-welded together using nickel strips. The PCB is secured with screws and fitted with thermal pads. A thermistor is attached to the battery cells for temperature monitoring.

The battery cell is sourced from LS, model SP526578SR, with a rated voltage of 3.87V, a capacity of 5Ah, an energy rating of 19.35Wh, and a charge cutoff voltage of 4.45V.
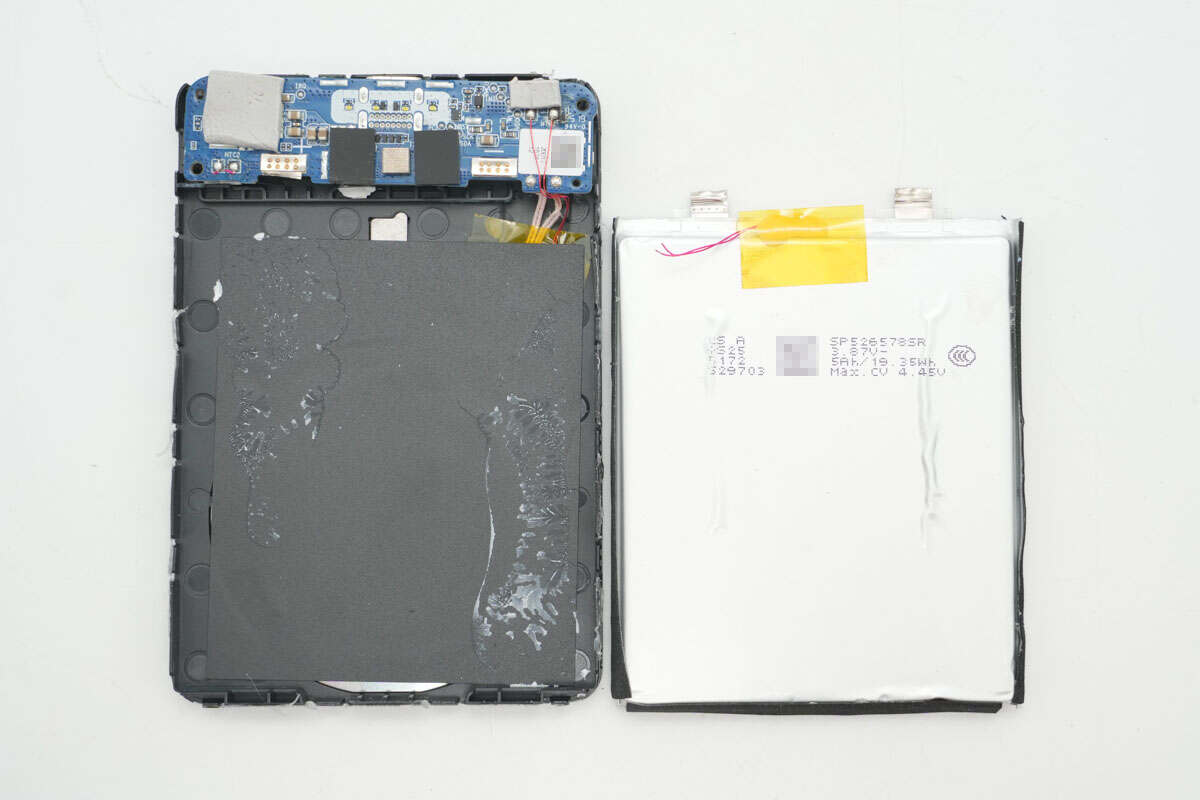

After removing the battery cell, an insulating isolation board is found underneath.
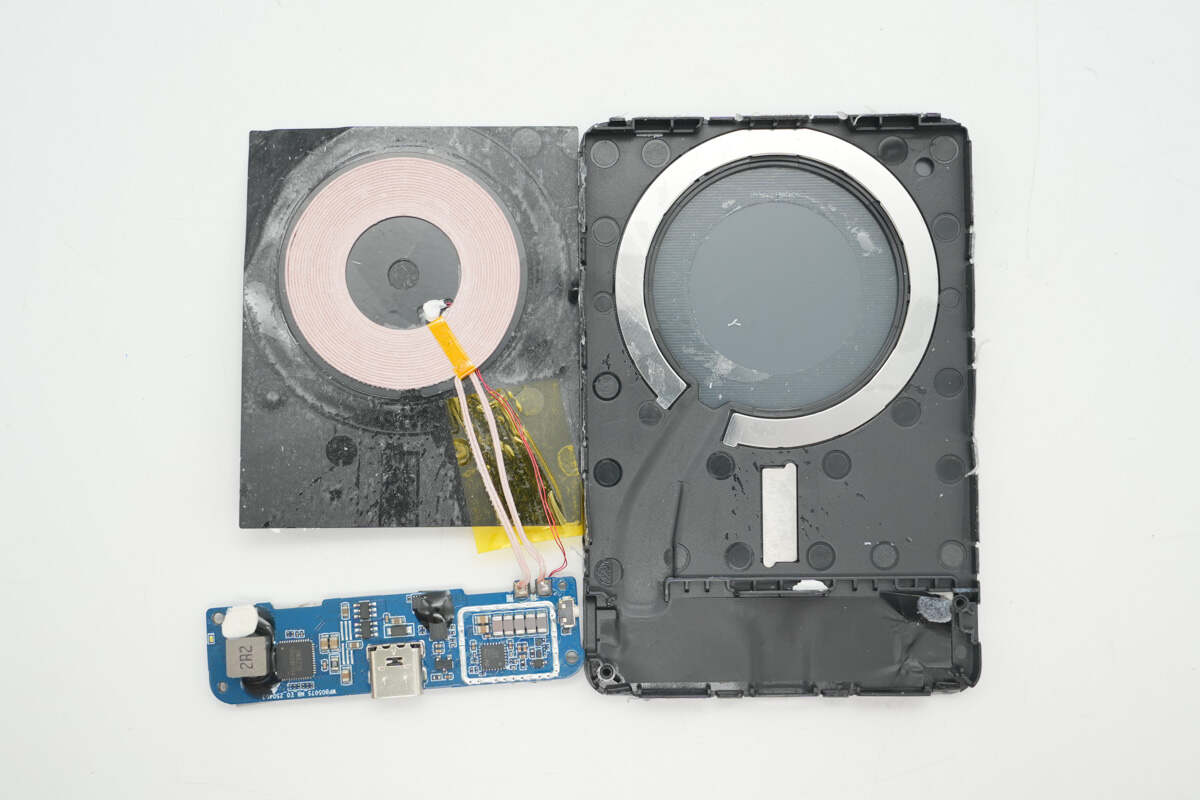

The other side of the insulation board is attached with the wireless charging coil, which also has a thermistor installed on it.
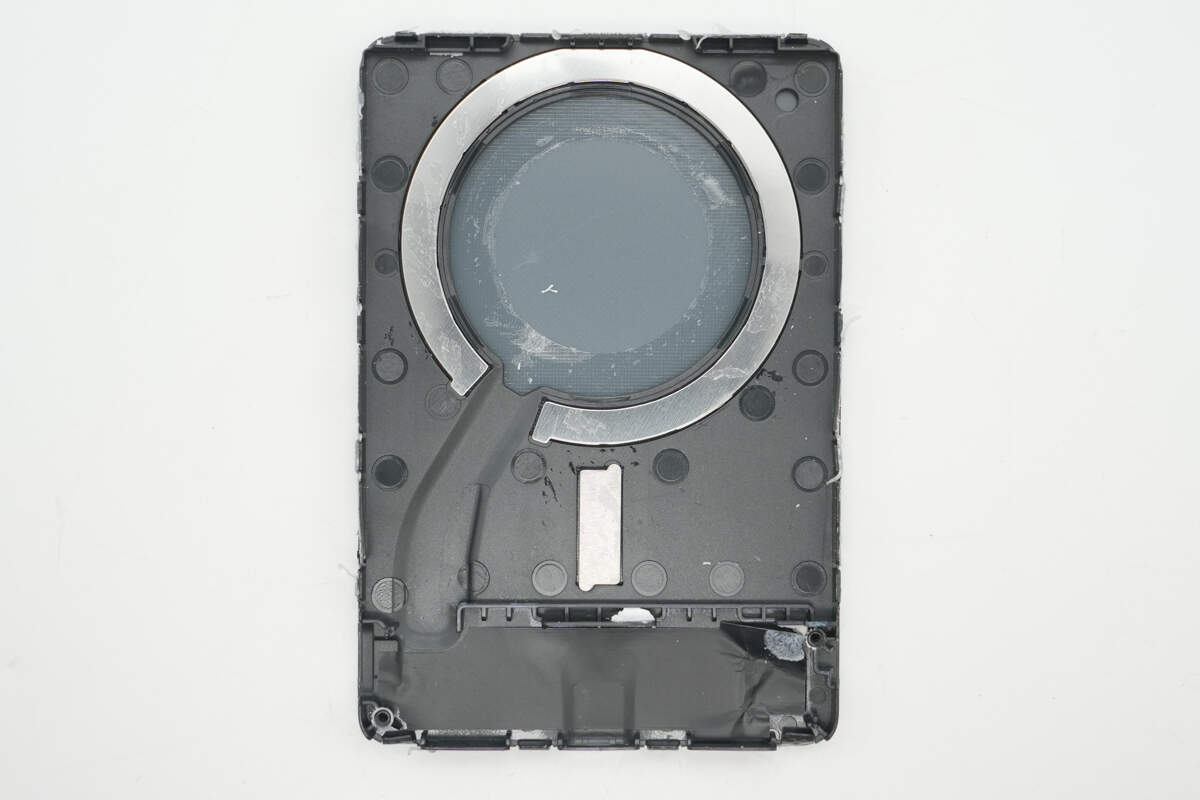

Inside the casing, there is a slot for securing the magnetic ring. The magnetic module uses 17 N52 magnets, providing a strong magnetic force of 10N.
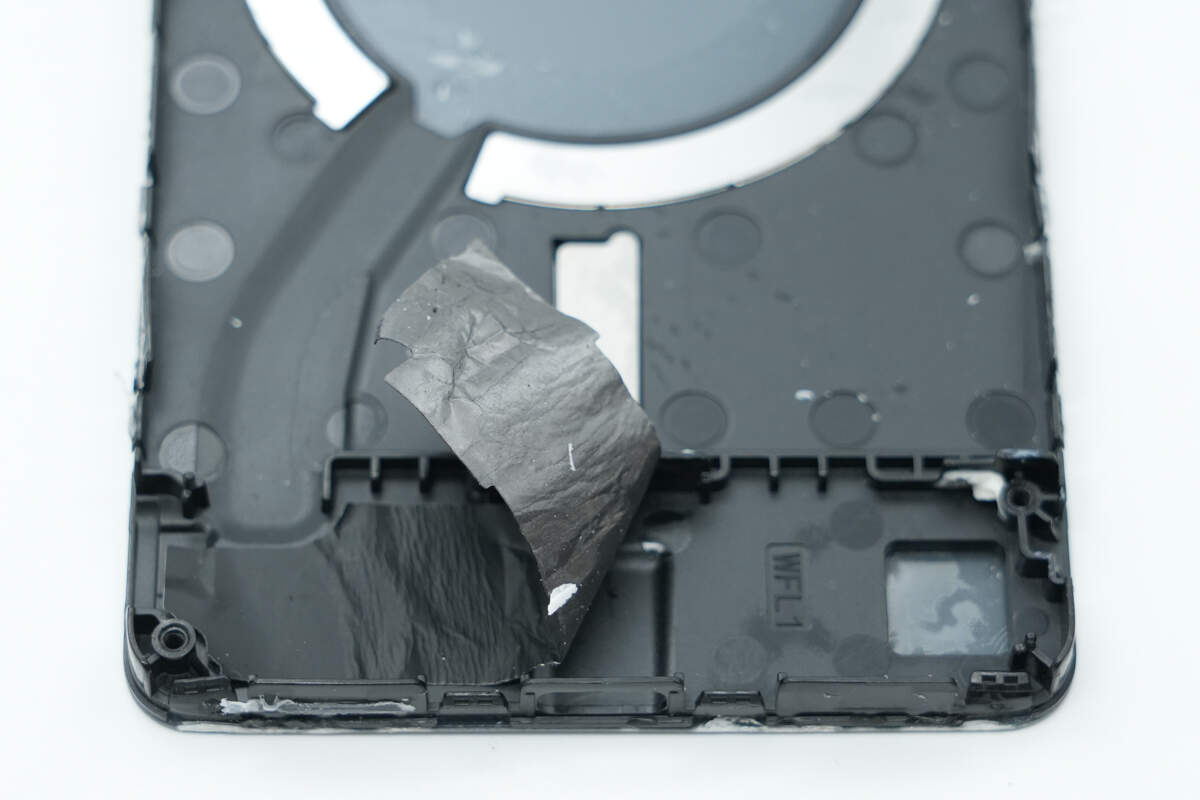

A graphite thermal pad is applied to the area corresponding to the PCB.
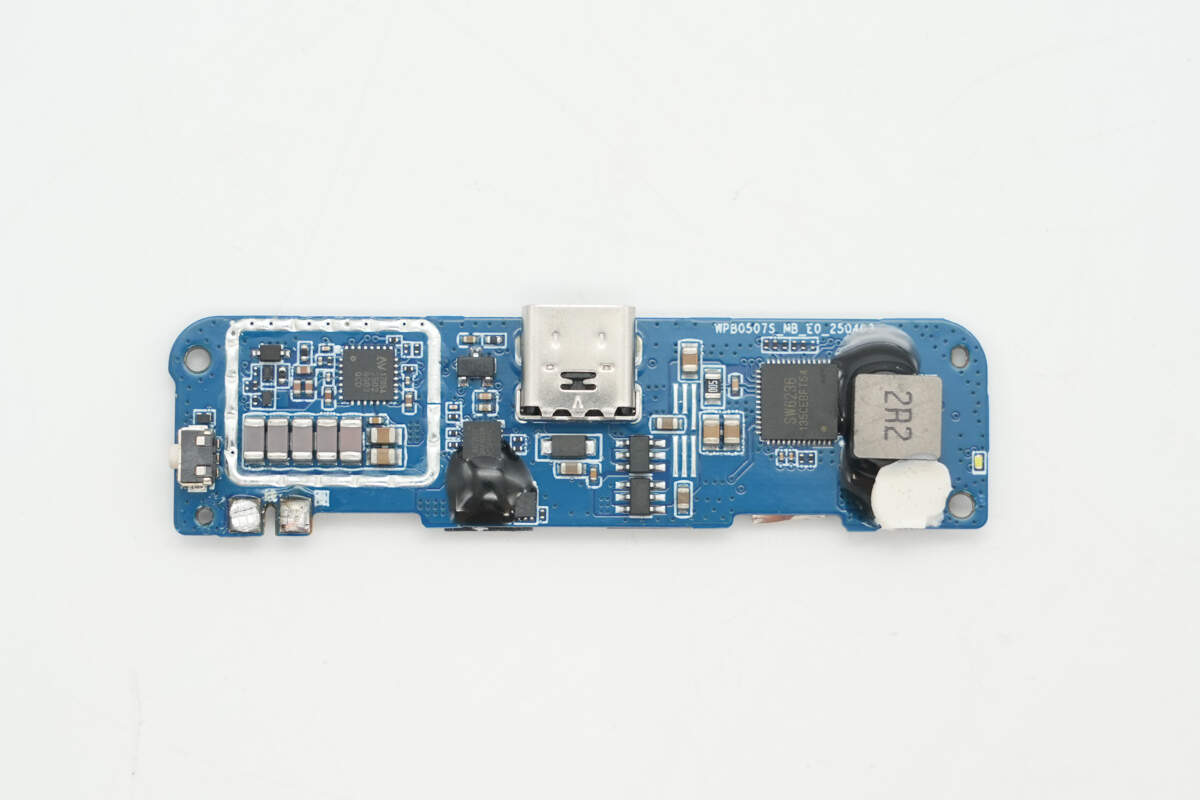

The front side of the PCB houses the master control chip, the wireless charging master control chip, the VBUS MOSFET, and other components. The lithium battery protection circuit and the inductor area are sealed with glue for protection.
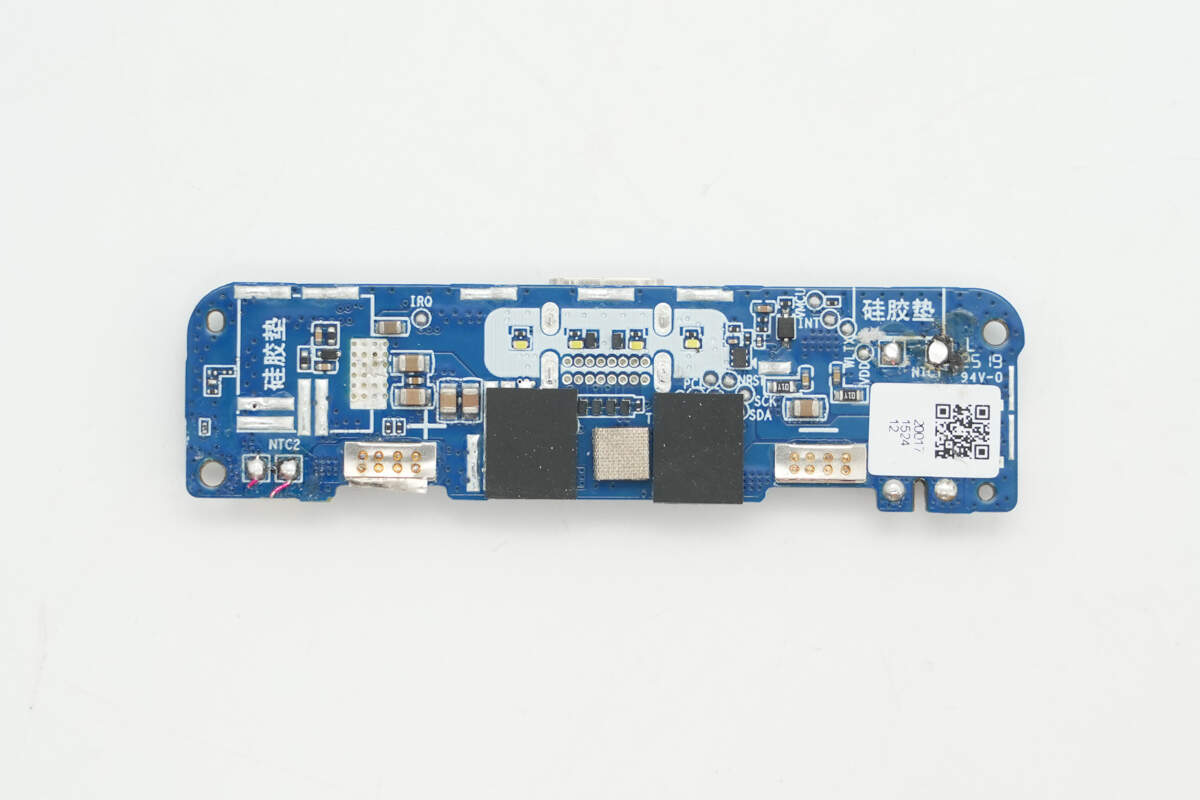
Here is a view of the back side.
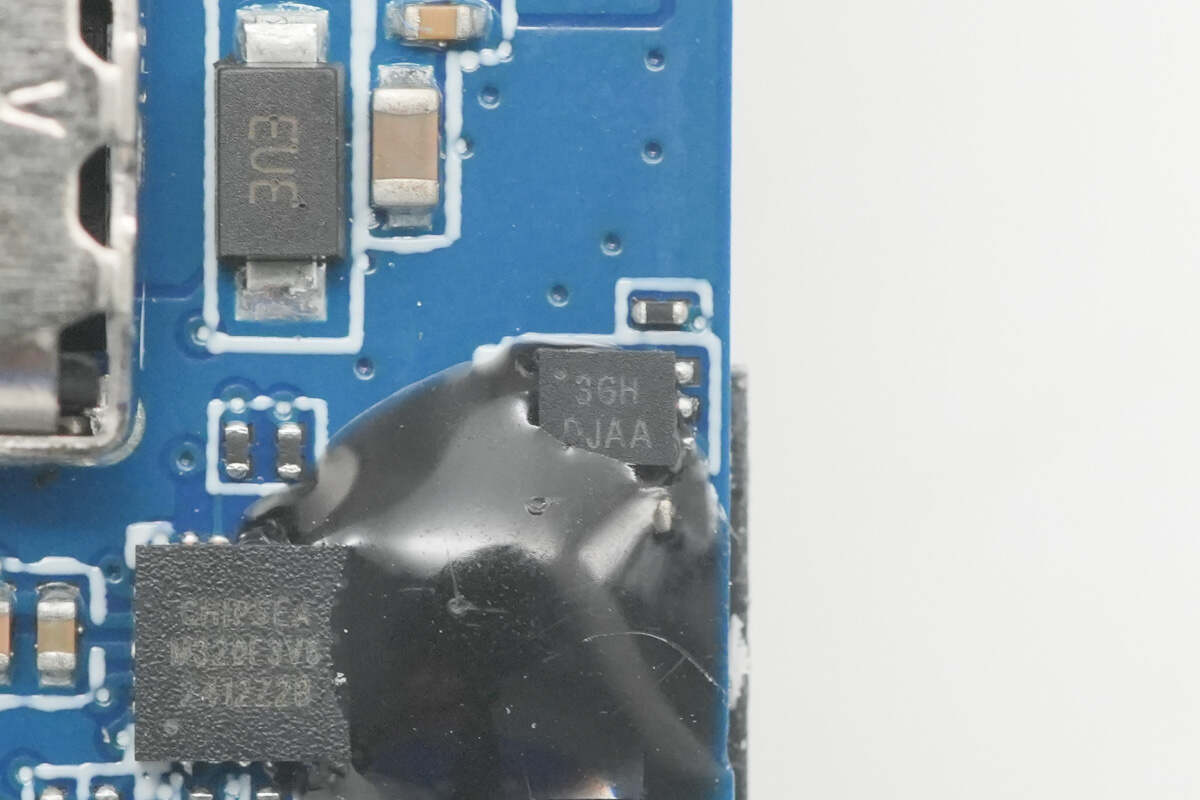

The lithium battery protection chip is from iCM, marked with "3GH," with the actual model number CM1003-GHD. This chip features built-in high-precision voltage detection and delay circuits. By monitoring the battery’s voltage and current, it protects against overcharging, over-discharging, and overcurrent. It is designed for protection circuits in single-cell lithium-ion or lithium polymer rechargeable batteries.
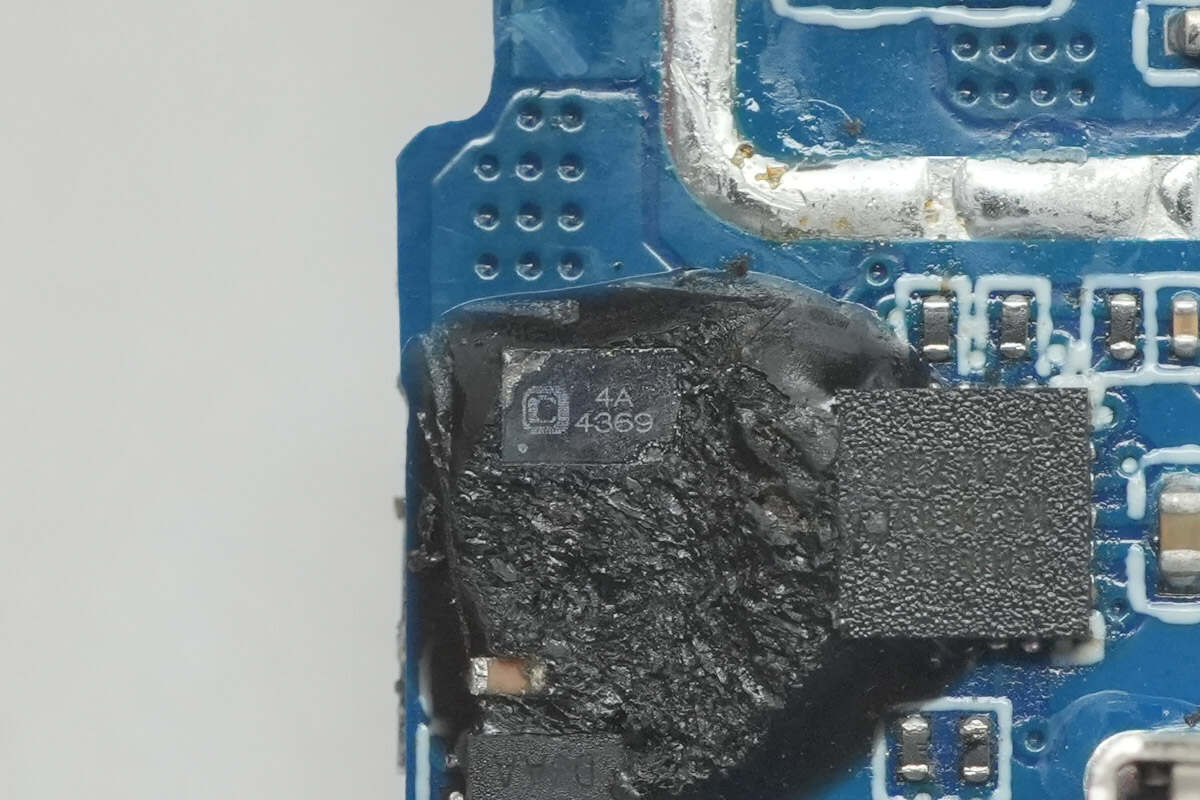

The protection MOSFET is marked with 4369.

The master control chip is from iSmartWare, model SW6236. It is a multi-port (A+A+C+C) multi-protocol power bank SoC that integrates a 5A high-efficiency switching charger and a built-in 22.5W high-efficiency synchronous boost output with an efficiency of up to 95.73%. Additionally, it features very low standby power consumption, less than 40μA at 3.7V. It supports fast charging on any of the four ports, with the two USB-C ports supporting bidirectional input and output. The chip is compatible with multiple mainstream fast charging protocols, including PPS, PD, SCP, FCP, QC, AFC, PE, and BC1.2, meeting the fast charging needs of most devices on the market.
The iSmartWare SW6236 supports both 3.6V/3.65V lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries and 4.2V/4.3V/4.35V/4.4V/4.5V ternary lithium batteries. It features an I²C interface that allows setting of charging current, output voltage, and output current limits. Additionally, it supports smart insertion detection, low current mode, and wireless charging mode. In wireless charging mode, it also supports fast charging while simultaneously discharging.

The SW6236 integrates a built-in coulomb counter for precise battery capacity measurement and a 12-bit ADC for high-resolution analog-to-digital conversion. It supports 3 to 5 LED battery indicators and also supports a 188-segment digital tube with fast charge indicators and a wireless charging icon, allowing users to easily monitor the device’s performance and status. Additionally, it offers multiple protection features, including OVP, OCP, UVP, OTP, CTP, and NTC temperature protection, ensuring high reliability.
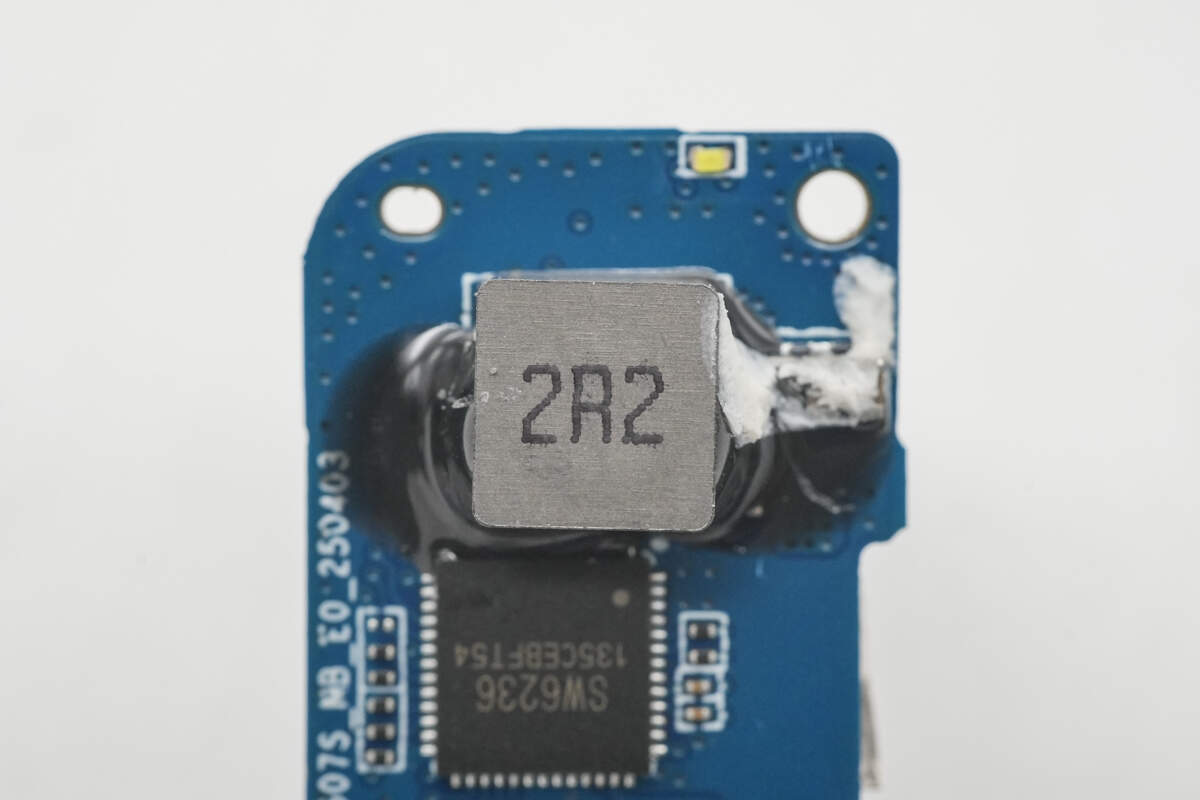

The 2.2μH alloy inductor is reinforced with adhesive for added stability.
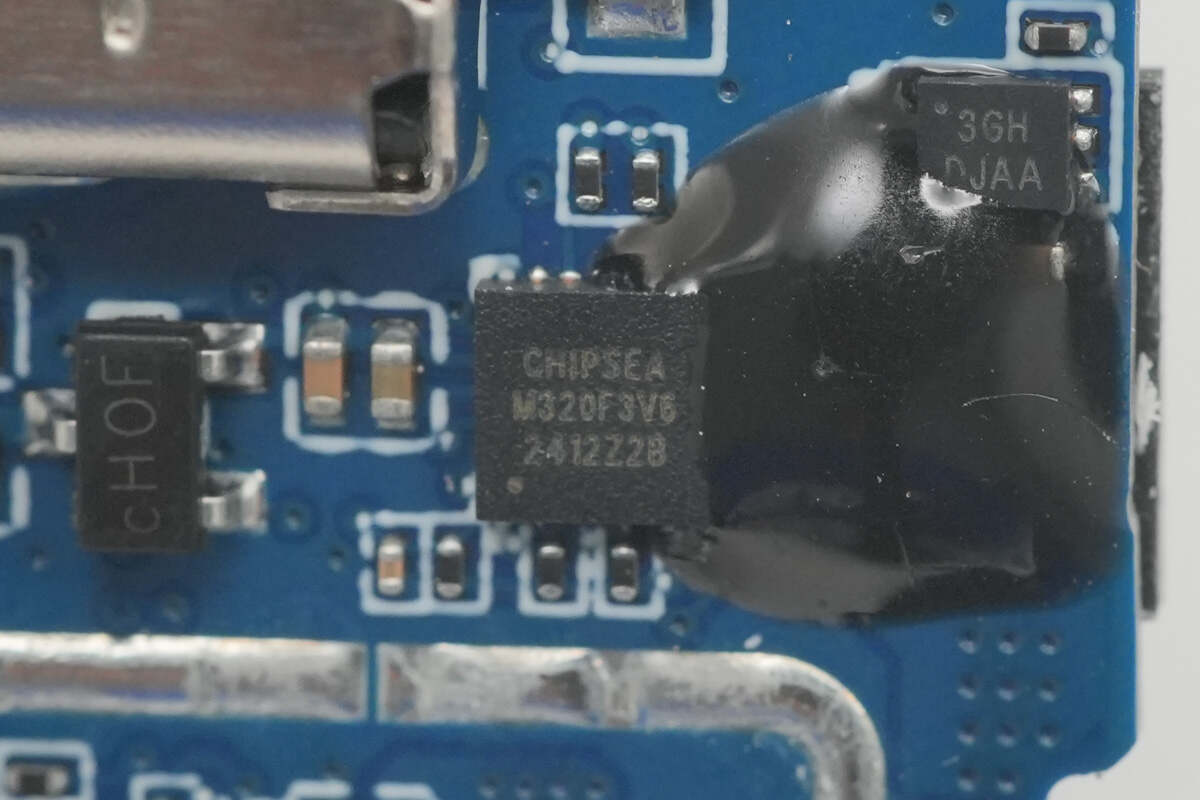
The MCU is from CHIPSEA, marked with M320F3V6, model CS8M320. It features 8K × 16-bit Flash memory and 488 bytes of SRAM, covering multiple products with 16 to 20 pins. This chip provides standard communication interfaces including I²C and UART, and is equipped with a 12-bit ADC, CVC, and timer functions. It comes in a QFN20 package.
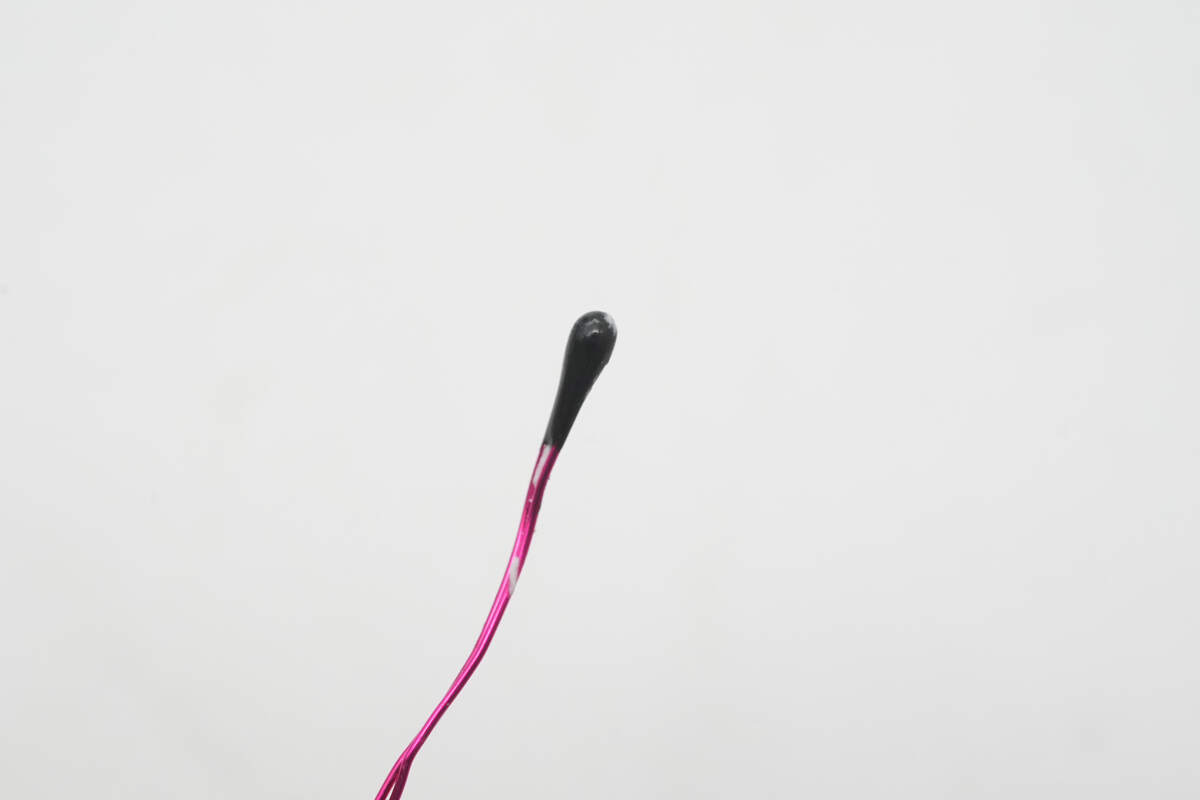

Close-up of the thermistor.
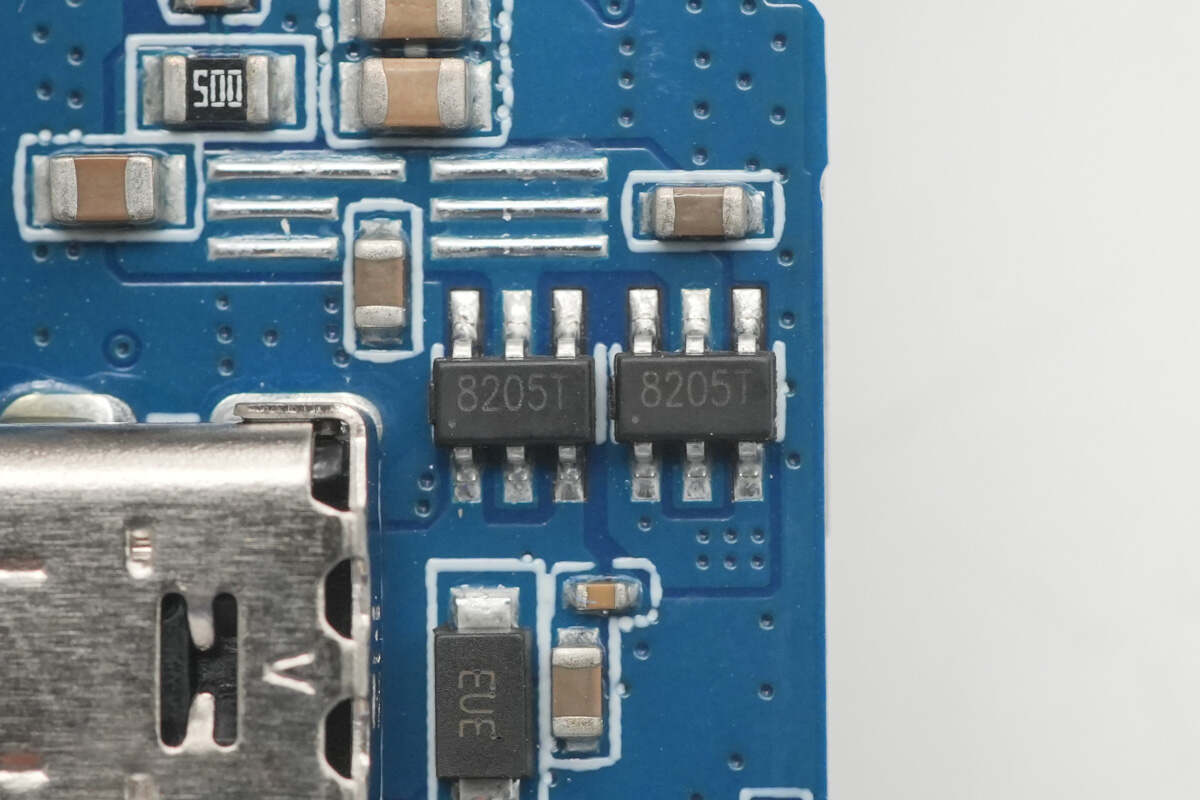
The USB-C VBUS MOSFETs use two MOSFETs marked with 8205T, connected in back-to-back series to prevent reverse current flow.
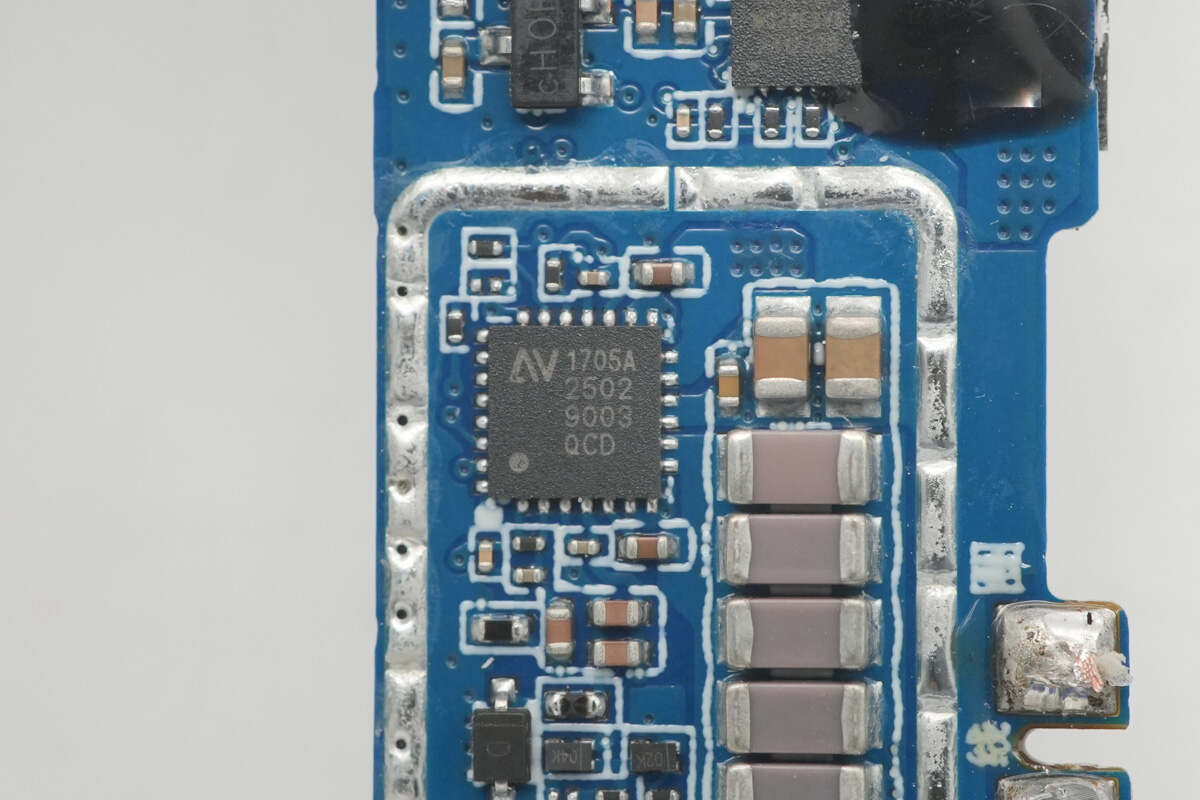
The wireless charging master control chip is from NuVolta, model NU1705A. It integrates a full-bridge power stage architecture suitable for a wide frequency range and a 32-bit MCU core. This power system integrates all key functional modules, including high-efficiency power MOSFETs, a low electromagnetic interference FET driver, bootstrap circuits, integrated 4.8V/1.8V LDO regulators, and lossless current sensing technology.
Its patented current sensing circuit provides accurate current readings for foreign object detection, power measurement, in-band communication, Q-factor detection, and digital demodulation functions. It also features multiple protection mechanisms: input undervoltage lockout, overvoltage protection, overcurrent protection, a unique Juggle Protection dynamic circuit, and thermal shutdown protection. These designs significantly enhance the overall system reliability. The chip comes in a 4mm × 4mm QFN package.
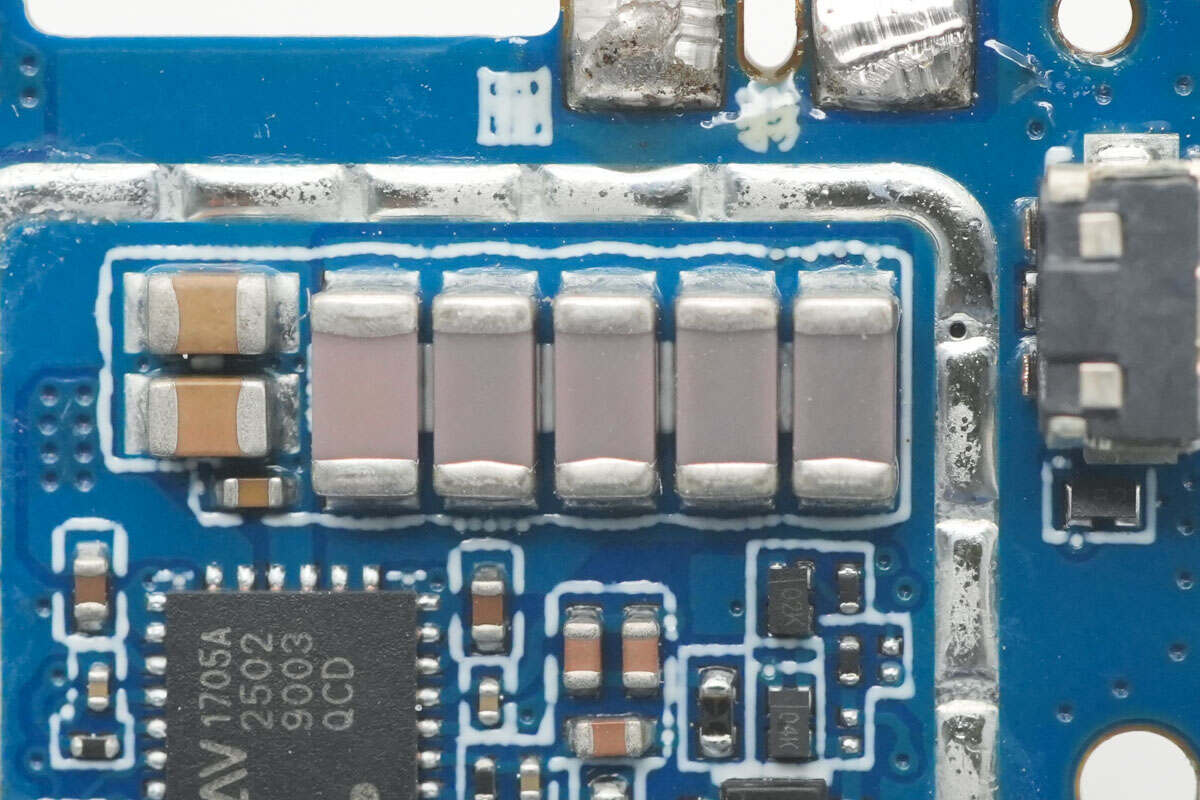
Close-up of the NPO resonant capacitors.
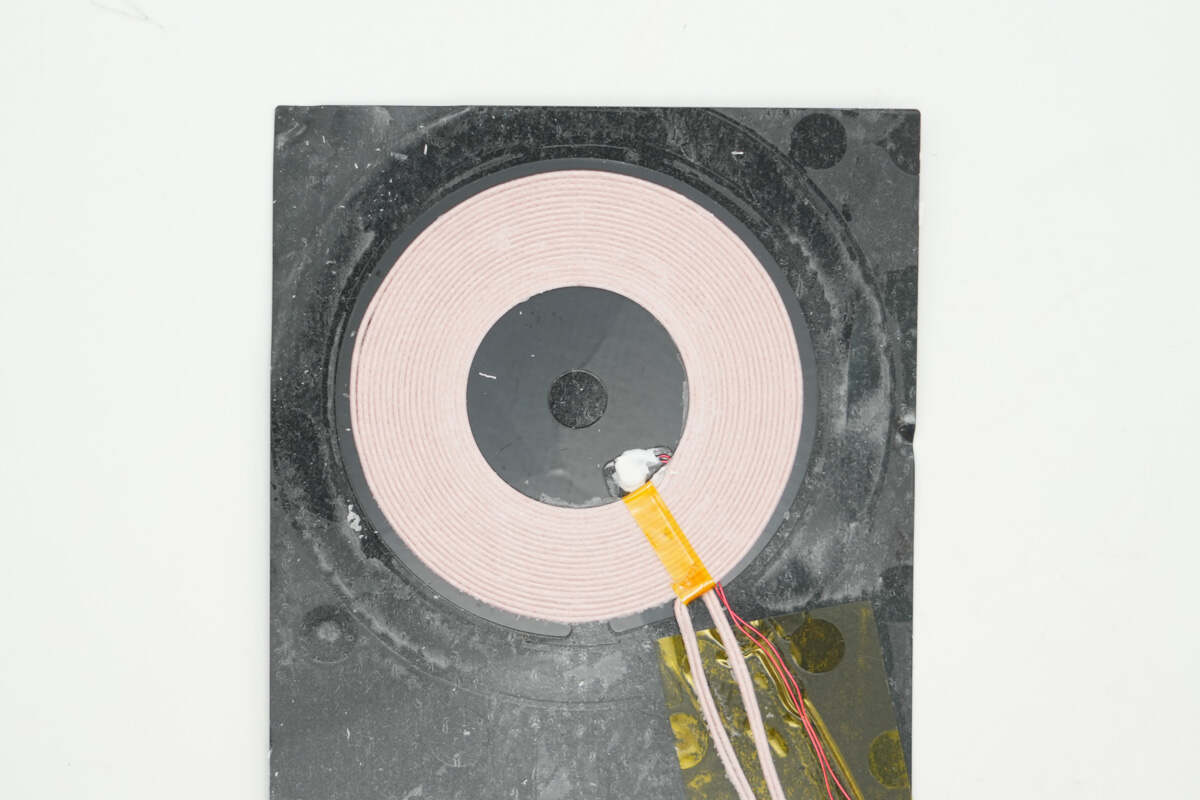

Close-up of the wireless charging coil.
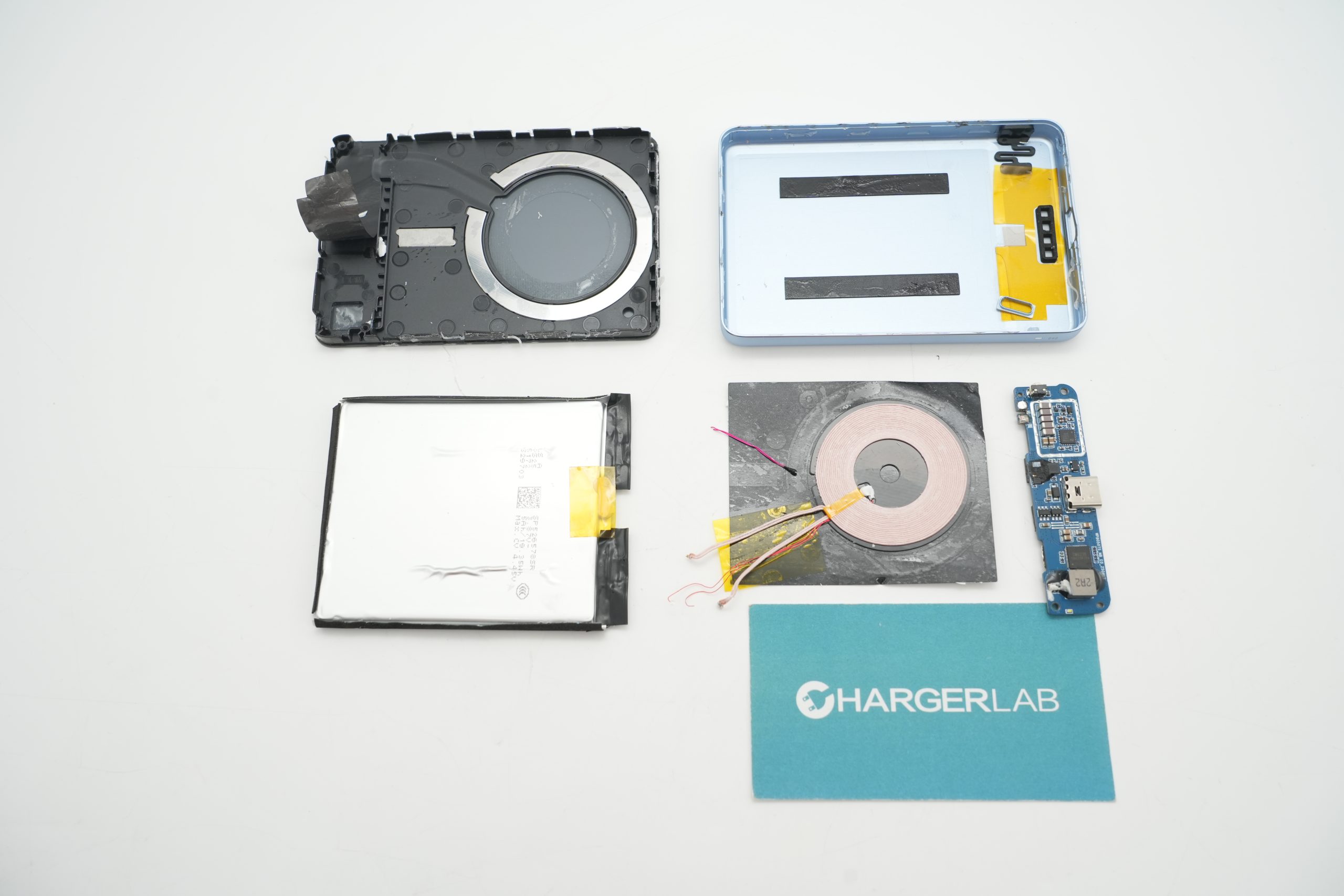

Well, those are all components of the Xiaomi 22.5W 5000mAh Magnetic Wireless Power Bank.
Summary of ChargerLAB
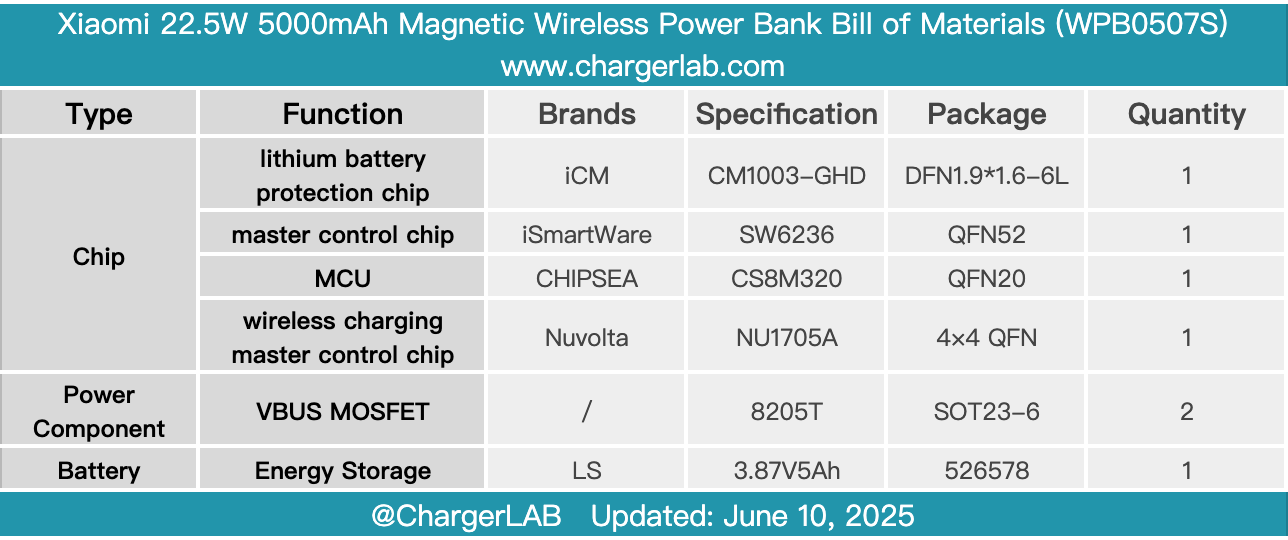
Here is the component list of the Xiaomi 22.5W 5000mAh Magnetic Wireless Power Bank for your convenience.
It features an aluminum alloy casing that ensures strength while keeping the texture lightweight. Combined with sandblasting and other fine finishing details, the design is exquisite. It is available in four colors: gold, purple, blue, and black. It supports 20W PD fast charging input, Xiaomi’s proprietary 22.5W fast charging output, and up to 15W wireless charging.
After taking it apart, we found that it uses LS battery cells and is equipped with an iCM lithium battery protection solution along with two thermistors for temperature monitoring. This setup enables temperature measurements at about 12,000 times per minute, effectively preventing issues such as overcharge, over-discharge, and overheating during the charging process.
The SoC solution uses the iSmartWare SW6236, whose high integration allows a single chip to handle both charging and discharging functions for the USB-C interface while ensuring excellent compatibility. Additionally, the NuVolta highly integrated wireless charging chip NU1705A is used to implement wireless charging functionality. Furthermore, the PCB is equipped with thermal pads and graphite thermal stickers to aid heat dissipation, and the battery cell is reinforced with double-sided adhesive.
Related Articles:
1. Teardown of HUAWEI 3000W R4850G1 Power Supply Unit
2. Teardown of CUKTECH 10 GaN Charger Ultra (AD1204U)
3. Teardown of Huawei WATCH 2nd-Gen Wireless SuperCharger (CW05)









