Introduction
Kilovolt high-voltage power modules are commonly used in outdoor chargers, industrial motor drives, photovoltaic inverters, energy storage, and other high-voltage, high-power applications. These scenarios often involve harsh working environments, making them susceptible to issues such as sun exposure, high temperatures, and moisture intrusion. Meanwhile, traditional power modules filled with silicone gel tend to experience substrate aging and deformation, even cracking, due to long-term temperature fluctuations in harsh conditions. Additionally, silicone gel easily absorbs moisture and impurities from the environment, which can cause substrate short circuits and pose significant challenges to system reliability.
Recently, Navitas has launched the SiCPAK power module featuring advanced epoxy resin encapsulation technology. This technology effectively blocks moisture intrusion and reduces the likelihood of substrate deformation caused by temperature changes, significantly enhancing system reliability.
Navitas Semiconductor SiCPAK Power Module
Navitas’s new SiCPAK power module adopts epoxy resin encapsulation technology combined with Navitas’s proprietary “groove-assisted planar gate” silicon carbide MOSFET technology. After undergoing rigorous design and comprehensive validation processes, it is specifically engineered for stable operation in high-power environments, offering superior reliability and high-temperature performance.
In terms of applications, the SiCPAK power module targets several key sectors, including electric vehicle DC fast charging (DCFC), industrial motor drives, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), photovoltaic inverters and power optimizers, energy storage systems (ESS), industrial welding, and induction heating markets. It is expected to accelerate technological advancements in these fields.
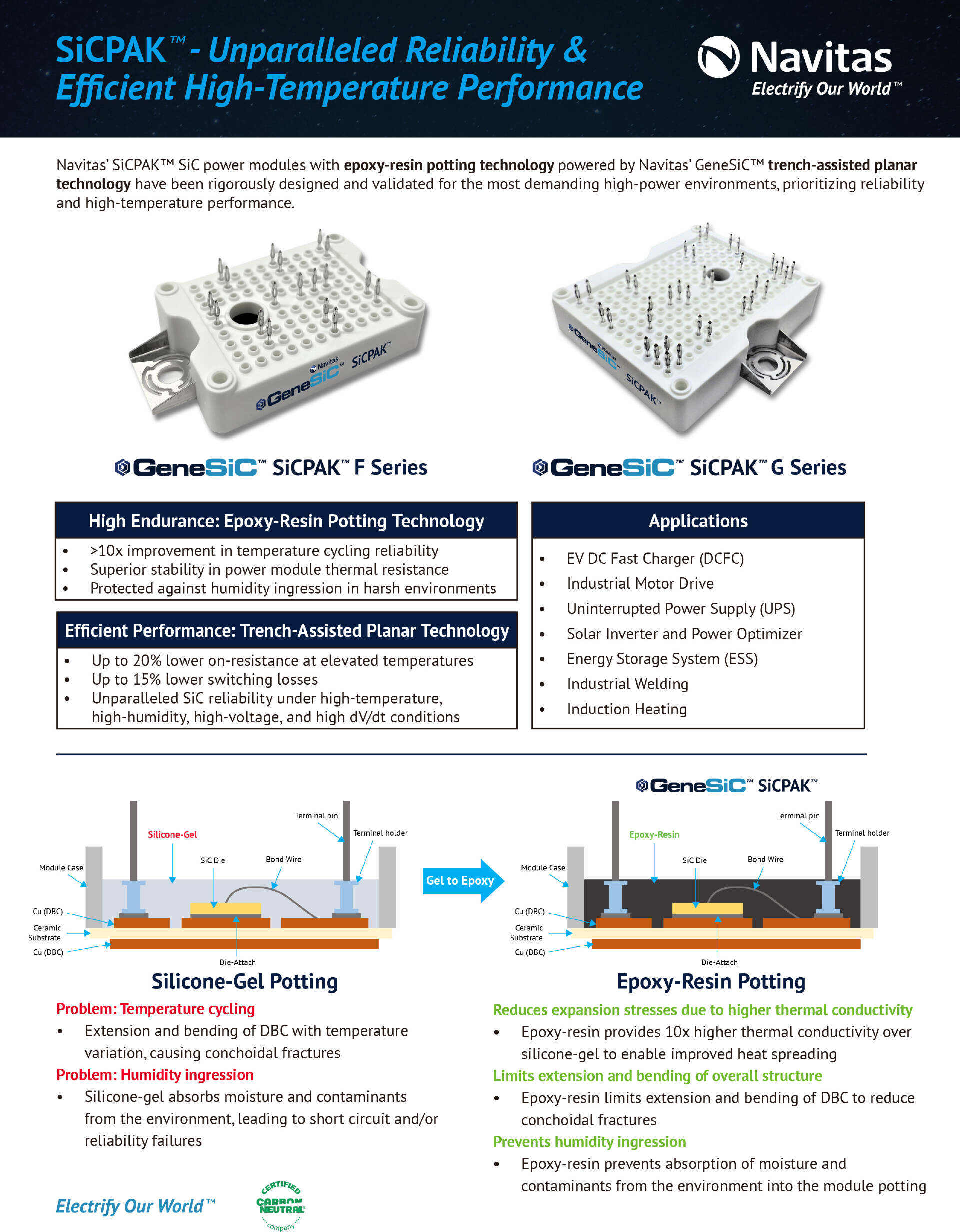
In terms of encapsulation technology, traditional silicone gel-filled modules are more prone to substrate stretching and bending caused by temperature fluctuations. Long-term thermal cycling can lead to wedge-shaped cracks. Additionally, silicone gel easily absorbs moisture and contaminants, which may result in performance degradation or even short circuits, posing reliability issues.
The Navitas SiCPAK power module, however, uses epoxy resin encapsulation. From a thermal management perspective, its thermal conductivity is ten times higher than that of silicone gel, effectively reducing heat accumulation. In terms of reliability, the epoxy resin restricts substrate expansion and bending, thereby reducing wedge cracking while preventing moisture and contaminant ingress.
Thermal shock tests conducted on power modules with silicone gel encapsulation and epoxy resin encapsulation reveal that after 1,000 cycles, the thermal resistance of silicone gel-filled modules increased by 80%, and isolation faults occurred. In contrast, modules with epoxy resin encapsulation only experienced a 15% increase in thermal resistance. This demonstrates that Navitas’s SiCPAK power module, employing epoxy resin encapsulation technology, significantly reduces substrate cracking, achieving stable thermal resistance and isolation withstand capability.

Regarding high-temperature performance, Navitas leverages over 20 years of innovation leadership in silicon carbide technology. Its GeneSiC groove-assisted planar gate MOSFETs exhibit lower losses, reduced operating temperatures, and superior robustness under high-temperature conditions, helping engineers build systems with long-term reliability. Comparative tests show that Navitas’s G3F devices have a smaller increase in on-resistance compared to other products and significantly outperform two other device types in high-temperature regions, demonstrating better performance and higher efficiency under elevated temperatures. Furthermore, all Navitas GeneSiC silicon carbide MOSFETs feature published 100% full avalanche testing capability, a 30% improvement in short-circuit withstand capability, and a tightly controlled threshold voltage distribution that facilitates parallel operation.
The Navitas SiCPAK power module incorporates an NTC thermistor and offers multiple product variants with on-resistance ranging from 4.6 to 18.5 mΩ. Packaging options include SiCPAK F and SiCPAK G, supporting different circuit configurations such as half-bridge, full-bridge, and three-phase photovoltaic inverters. The modules are pin-to-pin compatible with industry-standard press-fit modules. Additionally, pre-applied thermal interface materials (TIM) are available to simplify assembly processes.
Summary of ChargerLAB
The newly launched Navitas SiCPAK power module offers superior high-temperature resistance and aging durability, effectively addressing the challenges of harsh environmental applications. Additionally, this module is compatible with existing industry-standard press-fit modules, featuring pin-to-pin compatibility for direct replacement of older modules, which facilitates new project development and routine maintenance for businesses.









